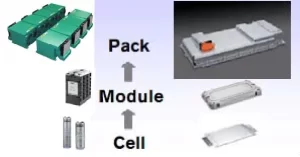
Knowing the nuances of battery technology is essential for effective content optimization. This article will delve into the basics of the differences between a battery cell, a battery module, and a battery pack. Exploring their definitions, designs, characteristics, and applications can illuminate the complex ecosystem that drives modern technology.
Part 1. Battery cell: Functions, design, and applications
What is a battery cell?
It is the basic unit of a battery, responsible for storing and releasing electrical energy. A battery cell comprises three primary components: the positive electrode (anode), the negative electrode (cathode), and the electrolyte. These elements work in concert to facilitate the flow of ions between electrodes during the charging and discharging processes. This flow of ions generates electrical current, which can be harnessed to power various devices and applications. A battery cell is the fundamental building block that enables portable power solutions across multiple industries and technologies.
Battery Design
Size
Battery cells come in different sizes, ranging from miniature cells used in small electronics like watches to more giant cells employed in electric vehicles. The size of the cell impacts its capacity and energy density, dictating its suitability for specific devices or systems.
Shape
Battery cells can have diverse shapes, including cylindrical, prismatic, and pouch designs. Cylindrical cells, commonly found in flashlights and laptops, offer a compact form factor and efficient packaging. Prismatic cells, with their rectangular shape, are often used in devices where space optimization is essential, like smartphones and tablets. Pouch cells, characterized by their flexibility, are suitable for applications requiring unconventional shapes or custom configurations.
Internal Chemistry
The internal chemistry of a battery cell determines its performance characteristics, including voltage, capacity, and cycle life. Different chemistries, such as lithium-ion, nickel-metal hydride, and lead-acid, offer varying trade-offs in terms of energy density, cost, and safety. Lithium-ion cells, for instance, are known for their high energy density and lightweight construction, making them ideal for portable electronics and electric vehicles.
Electrode Materials
The choice of electrode materials significantly influences a battery cell’s overall performance and longevity. Common electrode materials include lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2), lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), and nickel manganese cobalt oxide (NMC). Each material has unique energy density, stability, and safety characteristics, allowing manufacturers to tailor cells to specific application requirements.
Packaging and Encapsulation
Battery cells are typically encased in protective packaging to safeguard against physical damage and environmental factors. The packaging material should provide adequate insulation and sealing to prevent leakage of electrolytes and ensure long-term reliability. Additionally, proper encapsulation helps mitigate safety risks associated with thermal runaway or short circuits.
Battery Applications
- Consumer Electronics: Battery cells power devices like smartphones, tablets, and laptops, enabling portable usage and on-the-go convenience.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Battery cells are crucial for EVs, providing the energy needed for propulsion and driving the shift towards sustainable transportation.
- Energy Storage Systems: Battery cells contribute to energy storage systems, storing excess energy from renewable sources like solar and wind for later use, enhancing grid stability and resilience.
- Portable Power Banks: Battery cells are used in power banks, offering convenient backup power for smartphones, tablets, and other mobile devices when the main power is unavailable.
- Medical Devices: Battery cells power various medical devices, such as portable monitors and infusion pumps, ensuring reliable operation and patient care in clinical settings.
Part 2. Battery control module: Functions, design, and applications
What is a Battery Control Module? (Battery Control Module Definition)
A Battery Control Module (BCM) is essential in modern battery management systems. It actively monitors, regulates, and protects battery cells within a battery pack. The BCM ensures efficient energy distribution, prolongs battery life, and enhances safety by preventing overcharging, overheating, and deep discharging.
Key Functions of a Battery Control Module:
- Monitors voltage, temperature, and current of battery cells.
- Balances charge among individual cells to maximize battery lifespan.
- Prevents battery pack failures caused by overcharging or deep discharging.
- Manages communication with external systems in EVs, energy storage, and industrial applications.
In electric vehicles, the BCM is crucial in optimizing performance and ensuring battery safety. It is often integrated with a Battery Management System (BMS), which oversees multiple modules in a larger battery pack.
Battery Control Module vs. Battery Management System (BCM vs. BMS)
| Feature | Battery Control Module (BCM) | Battery Management System (BMS) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Regulates individual battery modules and ensures safe operation. | Manages the entire battery pack, including multiple modules. |
| Key Components | Voltage and temperature sensors, microcontroller, balancing circuits. | Multiple BCMs, data processing units, cooling systems. |
| Applications | Electric vehicles, energy storage, marine propulsion. | Large-scale battery packs in EVs, grid storage, industrial applications. |
Common Battery Control Module Issues & Troubleshooting
A faulty BCM can lead to inefficient battery performance or even system failure. Here are some common issues and solutions:
- Battery Not Charging Properly: Check for faulty voltage sensors or software misconfiguration.
- Overheating Battery Pack: Ensure thermal management components like cooling fans are working.
- Unexpected Battery Drain: Test for a short circuit or faulty cell balancing.
- EV Display Showing Battery Error: Scan the BCM for diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and reset if needed.
Part 3. Battery pack: Functions, design, and applications
What is a battery pack?
A battery pack is a collection of individual cells or modules arranged in a specific configuration to provide a unified power source. These cells or modules are typically interconnected and housed within a protective enclosure, ensuring safe and efficient operation. The arrangement of cells or modules within the lithium-ion battery pack is carefully designed to optimize performance, capacity, and voltage output for the intended application. Battery packs are commonly used in various devices and systems, including electric vehicles, portable electronics, and energy storage systems, to deliver reliable and consistent power supply.
Battery Design
Battery Cell Arrangement:
- Determine the required voltage and capacity for the application.
- Select the appropriate type and size of battery cells (e.g., lithium-ion, lithium-polymer) based on the performance requirements.
- Decide on the arrangement of cells, including series and parallel configurations, to achieve the desired voltage and capacity.
- Ensure uniformity in cell specifications and characteristics to maintain balance and consistency in the pack.
Housing Design:
- Choose suitable materials for the battery pack housing that provide adequate strength, durability, and thermal management.
- Design the housing to accommodate the arrangement of battery cells and modules, ensuring efficient use of space.
- Incorporate features such as cooling vents, heat sinks, or thermal insulation to regulate temperature and prevent overheating.
- Implement measures to protect the battery cells from physical damage, moisture, dust, and other environmental factors.
Safety Features:
- Integrate a Battery Management System (BMS) to monitor and manage the charging and discharging process, cell balancing, and temperature control.
- Include built-in protections against overcharging, over-discharging, short circuits, and thermal runaway.
- Install safety devices such as fuses, circuit breakers, or disconnect switches to isolate the battery pack in emergencies.
- Ensure compliance with safety standards and regulations, such as UN/DOT transportation regulations and UL certifications.
Electrical Connections:
- Design the electrical connections between battery cells, modules, and external terminals with low resistance to minimize energy loss and maximize efficiency.
- Use high-quality conductive materials and connectors that provide reliable and secure connections, reducing the risk of voltage drops or electrical faults.
- Implement proper insulation and shielding to prevent electrical arcing, corrosion, and electromagnetic interference.
Testing and Validation:
- Conduct thorough testing of the battery pack design to verify performance, safety, and reliability under various operating conditions.
- Perform stress tests, including temperature cycling, vibration, shock, and electrical load testing, to assess durability and endurance.
- Validate compliance with industry standards and customer requirements through rigorous testing protocols and certification processes.
Battery Applications
- Portable Electronic Products: Battery packs are widely used in mobile electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops, providing convenient and on-the-go power solutions for consumers.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Battery packs serve as electric vehicles’ primary energy storage system, supplying the power needed for propulsion and enabling emission-free transportation.
- Stationary Energy Storage Solutions: Battery packs are deployed in stationary energy storage systems to store excess energy generated from renewable sources like solar and wind, providing backup power, grid stabilization, and load-shifting capabilities.
Part 4. Battery cell vs battery module vs battery pack: What is the difference?
Battery Cell
A battery cell is the basic building block of a battery, consisting of electrodes, electrolytes, and a casing. It is the smallest unit capable of storing and releasing electrical energy through chemical reactions.
Battery Module
A battery module is a collection of interconnected cells housed within a single enclosure. It typically includes cooling systems, voltage monitoring circuits, and structural support elements. Battery modules allow for scalability and customization of battery packs by combining multiple cells to meet specific energy and power requirements.
Battery Pack
A battery pack, also known as a battery pack or battery assembly, comprises one or more battery modules or cells arranged in series or parallel configurations. It integrates components such as battery management systems (BMS), thermal management systems, and safety features to provide a complete power solution for a specific application. Battery packs are commonly used in electric vehicles, energy storage systems, and portable electronics, offering higher voltage, capacity, and energy density than individual cells or modules.
Part 5. FAQs
What is the difference between a battery module and a battery pack?
A battery module is a group of individual battery cells connected, usually with their management system. On the other hand, a battery pack consists of one or more modules, along with additional components like casing, connectors, and thermal management systems.
What is a cell in a battery pack?
A cell in a battery pack refers to the individual battery unit that stores and releases electrical energy. These cells are typically cylindrical or prismatic in shape. They are connected in series or parallel to achieve the desired voltage and capacity for the pack.
What is a modular battery pack?
A modular battery pack is a battery pack design that consists of multiple interchangeable modules. These modules can be easily replaced or upgraded, offering flexibility and scalability in capacity and configuration.
What is a cell vs pack vs module?
A cell is the basic unit of a battery, while a module is a group of cells connected. On the other hand, a pack includes one or more modules and additional components necessary for operation, such as casing, connectors, and control electronics.
What is the difference between a pack and a module?
The main difference between a pack and a module is their scale and complexity. A module is a smaller unit consisting of interconnected cells. At the same time, a pack is a larger assembly that includes one or more modules along with additional components for functionality and safety.
What are the symptoms of a bad battery control module?
Common symptoms of a faulty battery control module include rapid battery drain, inconsistent charging, overheating battery packs, and error codes displayed in electric vehicles or energy storage systems.
How does a battery control module work?
A battery control module monitors and manages voltage, temperature, and current flow in a battery module. It ensures safe and efficient energy distribution by balancing charge among cells and preventing overcharging or overheating.
Can a battery control module be replaced?
Yes, a battery control module can be replaced if it fails. However, it may require reprogramming or recalibration to match the specific battery system it controls.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Paper Battery vs. Flexible Battery: What’s the Difference and Which Is Better?
Paper vs. flexible batteries: learn the key differences, benefits, and which power source fits best for wearables, sensors, and smart tech.
What to Know Before Buying a Tiny LiPo Battery for Your Project
Tiny LiPo batteries are powerful and compact. Learn how to choose the right one for your project with specs, safety, and charging tips.
Bloated LiPo Battery: Will It Explode?
Will a bloated LiPo battery explode? Discover the causes, risks, safety steps, and expert tips to avoid disaster and protect your gear. Must-read safety guide!
12V 100Ah Lithium Ion Battery Price: Full Guide
Learn about 12V 100Ah lithium-ion battery price, from cost ranges to best brands, hidden fees, and how to get the best deal. A must-read for smart buyers!
Resistance and Conductivity: What It Means for Your Lithium Batteries
Resistance and conductivity impact lithium battery performance, lifespan, and safety—learn how they work and why they matter.