- Part 1. Overview of rechargeable battery technologies
- Part 2. Silver zinc battery – High power for specialized applications
- Part 3. Lithium-ion rechargeable battery – Long life for everyday electronics
- Part 4. Comparing silver zinc and lithium-ion batteries
- Part 5. FAQs about silver zinc and lithium-ion rechargeable batteries
Choosing the right rechargeable battery—whether a high-power silver zinc battery or a long-life lithium ion rechargeable battery—requires understanding energy density, cycle life, safety, cost, and specific application scenarios. This guide helps engineers, hobbyists, and consumers select the optimal cell for each use case.
Part 1. Overview of rechargeable battery technologies
Rechargeable batteries power devices from tiny medical implants to electric aircraft. Silver-zinc and lithium-ion chemistries dominate high-performance applications. Understanding their trade-offs helps you match battery type to your scenario.
- Cost vs Performance: Total cost per kWh over lifespan, crucial for EV and drone projects.
- Energy Density: Important for space-constrained devices like wearables and UAVs.
- Cycle Life: For products with frequent charging, e.g., EVs or laptops.
- Safety Requirements: Mission-critical, medical, or military applications.
- Temperature Range: Extreme environments.
Quick Comparison: Silver-zinc excels in ultra-high power and safety, but shorter lifespan. Lithium-ion offers long cycle life and fast recharge, widely supported in consumer electronics.
Part 2. Silver zinc battery – High power for specialized applications
Scenario: Best for medical implants, aerospace, and high-performance drones requiring high energy in compact, safe cells.
- Cathode: Silver oxide (AgO)
- Anode: Zinc (Zn)
- Electrolyte: Alkaline solution (KOH)
Advantages:
- High energy output for high-drain applications.
- Lightweight and compact design.
- Inherently safe with low risk of leakage or explosion.
- Environmentally friendly and easier to recycle.
Disadvantages:
- Higher production cost due to silver content.
- Shorter lifespan (150–300 cycles).
- May require more frequent replacement.
Common Applications:
- Military communication devices and critical tools.
- Spacecraft instruments and aerospace systems.
- Portable medical equipment and implants.
- Hearing aids for small size and high power.
- High-performance drones needing lightweight, high-energy batteries.
Storage & Maintenance Tips:
- Store at 40–60% state-of-charge to minimize capacity fade.
- Avoid temperatures above 45°C to prevent zinc corrosion.
- Perform shallow discharge cycles monthly when in storage.
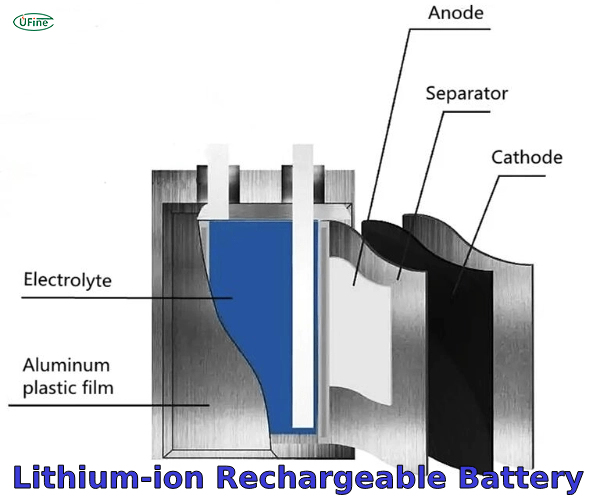
Part 3. Lithium-ion rechargeable battery – Long life for everyday electronics
Scenario: Ideal for smartphones, laptops, EVs, power tools, and renewable energy storage due to long cycle life and high energy density.
- Anode: Carbon-based materials (graphite, lithium titanate, or silicon)
- Cathode: Lithium metal oxides (LiCoO2, LiFePO4, LiMn2O4)
- Electrolyte: Lithium salt in organic solvent or polymer
Advantages:
- High energy density for longer run times between charges.
- Lightweight and compact design suitable for portable devices.
- Low self-discharge rate allows for extended shelf life.
- Fast recharge compared to other battery types.
Disadvantages:
- Susceptible to aging and reduced capacity over time.
- Risk of thermal runaway and fire if mishandled or damaged.
- More expensive to produce than some other battery types.
- Requires protection circuitry to prevent overcharging and over-discharging.
Environmental Considerations: Manufacturing consumes significant energy and often involves cobalt mining. Advances in cathode chemistry (e.g., NMC811, LFP) reduce cobalt usage and improve sustainability.
Common Applications:
- Smartphones and tablets for high energy density and compact size.
- Laptops and notebooks for portable power.
- Electric vehicles with large lithium-ion packs for propulsion.
- Power tools such as cordless drills and saws.
- Renewable energy storage systems (solar panels, wind turbines).
Future Trends:
- Solid-State Electrolytes: Ultra-high energy density and zero flammability.
- Silicon-Dominant Anodes: Enabling >400 Wh/kg cell energy.
- Recycling Innovations: Closed-loop recovery targeting >90% material reuse.
Part 4. Comparing silver zinc and lithium-ion batteries
| Parameter | Silver-Zinc | Lithium-Ion |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density (Wh/kg) | 100–150 | 150–250 |
| Cycle Life | 150–300 cycles | 500–1000+ cycles |
| Nominal Voltage | 1.5 V | 3.6–3.7 V |
| Charge Rate | 0.2–0.5 C | 1–2 C (fast charge) |
| Recycling | Easy, less toxic | Challenging, cobalt & lithium recovery |
Use-Case Comparison
- Medical Implants: Silver-Zinc preferred for safety, low voltage, and biocompatibility.
- Consumer Electronics: Lithium-Ion dominates with long cycle life and thin form factors.
- Aerospace & Defense: Silver-Zinc selected when mission-critical safety outweighs lifespan.
- Electric Mobility: Lithium-Ion chosen for cost per cycle and fast charging infrastructure.
Part 5. FAQs about silver zinc and lithium-ion rechargeable batteries
Are lithium batteries rechargeable?
Yes, lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable and can last 500–1000+ cycles depending on usage and protection circuitry.
Are zinc batteries better than lithium-ion batteries?
It depends on the application. Zinc (silver-zinc) batteries excel in high-power, safety-critical devices but have shorter lifespan than lithium-ion batteries.
Will zinc batteries replace lithium-ion batteries?
Unlikely. Zinc batteries complement lithium-ion in safety-critical and high-power applications rather than fully replacing them.
Are silver-zinc batteries rechargeable?
Yes, silver-zinc batteries can be recharged for approximately 150–300 cycles before capacity drops below 80%.
How long do zinc batteries last?
Typical silver-zinc batteries last 150–300 cycles or 3–5 years shelf life under standard conditions.
Related Tags:
More Articles

고방전 배터리는 높은 전류와 발열로 배터리수명이 줄어듭니다. 구조적 한계, 사용 패턴, 충전 습관 등 실제 수명 단축 요인을 체계적으로 분석했습니다.
Capacitor vs Battery: What is the Difference?
Capacitor vs battery explained in detail. Learn the difference between capacitor and battery in energy storage, charging speed, lifespan, and real applications.
18650 Battery vs AA: Which Is Better for Your Device?
Compare 18650 vs AA batteries in capacity, voltage, rechargeability, and applications. Learn which battery type fits high-drain or everyday devices.
What is the Difference Between Battery Cell, Battery Control Module, and Battery Pack?
Compare battery cells, modules, and packs. Learn functions, design differences, control modules, and selection tips for EV, ESS, and industrial use.
How to Prevent LiPo Battery Explosion?
Can LiPo batteries explode or catch fire? Learn key causes of LiPo battery fires and proven charging, storage, and handling tips to reduce explosion risk.