- Part 1. Learn about lithium battery short circuit
- Part 2. Why do lithium batteries short circuit?
- Part 3. What happens if you short a lithium battery
- Part 4. How to know if a lithium battery is short-circuited?
- Part 5. What should you do if a lithium battery is short-circuited?
- Part 6. Can improper use cause a lithium battery short circuit?
- Part 7. How to use lithium batteries correctly to prevent short circuits?
- Part 8. How does Ufine avoid short circuits in lithium batteries?
- Part 9. FAQs
Part 1. Learn about lithium battery short circuit
To understand a lithium battery’s short circuit, we first need to understand how the battery works.
How lithium batteries work
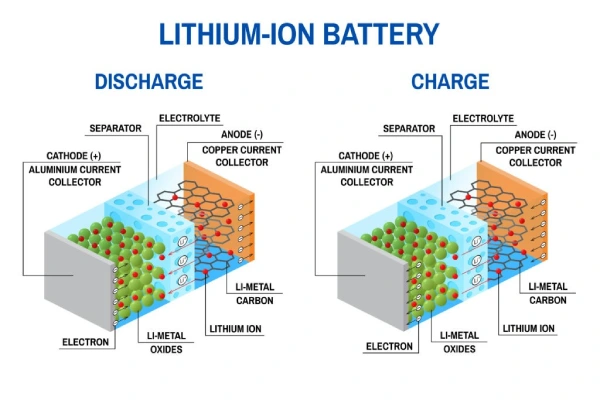
Lithium batteries convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. During normal operation, an electrochemical reaction occurs at the battery’s two electrodes: a reduction reaction occurs at the cathode, and an oxidation reaction occurs at the anode.
During the discharge process, the positive electrode is the cathode, and the negative electrode is the anode. During the charging process, the roles of the two poles are reversed; the positive pole is the anode, and the negative pole is the cathode.
An electrode releases electrons into the circuit. At the same time, the other electrode picks up electrons from the circuit. This overall favorable chemical reaction drives the flow of electricity in the circuit.
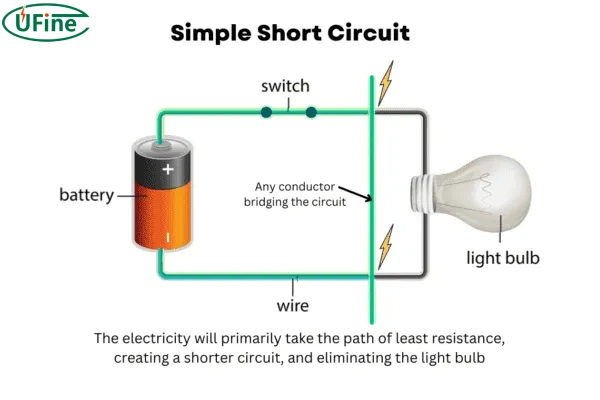
What is Li-ion battery short circuit?
The so-called short circuit means that electrons do not flow through the circuit connected to the electrical equipment, but directly flow between the two electrodes. Since these electrons do not have to do mechanical work, the resistance is very small.
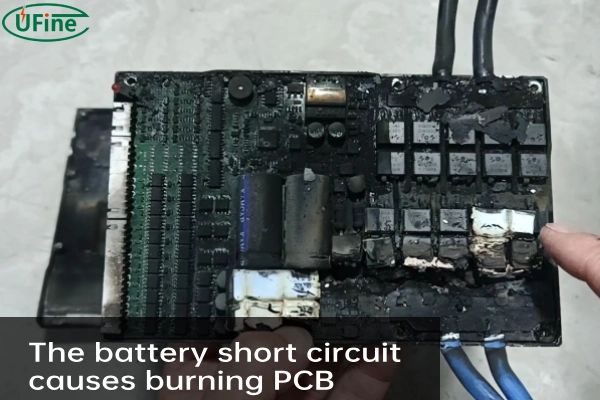
The chemical reaction accelerates, and the battery begins to self-discharge, losing chemical energy without doing any useful work. The extremely strong current during a short circuit will cause the battery resistor to heat (Joule heat), which will likely damage the device.
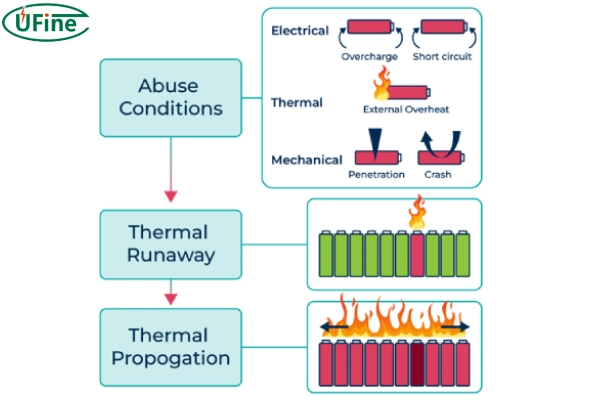
A shorted battery is a bad failure. The chemical energy stored in the battery is lost as heat and cannot be used by the device. At the same time, a short circuit can also cause severe heating. This will reduce the performance of the battery material and may even cause a fire or explosion by triggering thermal runaway.
Part 2. Why do lithium batteries short circuit?
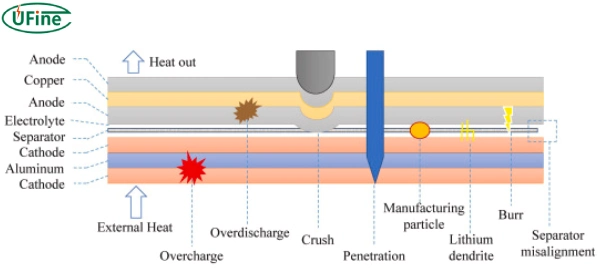
There are many reasons for the short circuit of lithium batteries. The following are common causes of short circuits of lithium batteries.
- Lithium battery electrolyte leakage. The internal sealing of the battery is poor, the electrolyte composition is inappropriate, the battery is damaged externally, etc.
- Lithium battery electrode material damage, Improper operation, material quality problems, external damage to the battery, etc.
- The battery separator is damaged. Improper operation, separator quality problems, external damage to the battery, etc.
- The lithium battery electrode is in contact with an external metal. Improper design of the lithium battery casing, quality issues with the casing material, external damage to the battery, etc.
- Short circuit during charging.g Improper design of lithium battery chargers, charger quality issues, incorrect use of chargers, etc.
- Short circuit during transportation. In Lithium batteries are squeezed, hit, etc., during transportation.
- Incorrect use. When lithium-ion batteries are exposed to special temperatures and humidity or are subject to impact, metal friction, or poor contact, the instantaneous current may be excessive, which may cause the battery to short-circuit and explode.
If you want to understand another common battery failure mode related to safety, read our guide on
👉 Understanding Battery Leaks: Why They Happen and How to Stay Safe
Since temperature plays a critical role in battery stability and failure risk, you may also find this article helpful:
👉 How Temperature Affects Battery?
Part 3. What happens if you short a lithium battery
1 Battery leakage
When the temperature inside the lithium battery rises slowly, the outer shell melts. Currently, the protective layer cannot provide protection, resulting in the leakage of corrosive electrolytes.
2 Lithium battery spontaneous combustion
When a lithium battery is short-circuited, a spark can ignite the electrolyte instantly. This is because the electrolyte consists of a flammable liquid. The burning electrolyte will ignite the plastic body and cause the lithium battery to burn. If there are flammable materials around the lithium battery, it will cause a fire.
3 Explosion
The temperature inside the lithium battery rises quickly because the outer shell does not gradually melt when the temperature rises slowly. As a result, the internal space of the battery is insufficient to accommodate the expanding gas under heating. Lithium batteries can explode due to excessive pressure.
Part 4. How to know if a lithium battery is short-circuited?
A lithium battery is likely short-circuited if it shows abnormal heat, rapid voltage drop, or fails to deliver power normally.
Common signs include:
- Abnormal heating
The battery becomes hot within seconds or minutes, even under light load or when idle.
- Sudden voltage collapse
Measured voltage drops close to 0 V or far below the nominal value.
- Rapid discharge
The battery drains extremely fast or cannot hold a charge.
- Swelling or deformation
Especially in lithium polymer batteries, internal short circuits may cause gas buildup.
- Protection circuit activation
For protected batteries, the BMS may cut off output entirely.
⚠️Important: If a battery heats up rapidly or emits smell/smoke, stop testing immediately and isolate it.
Part 5. What should you do if a lithium battery is short-circuited?
If a lithium battery is short-circuited, immediately disconnect it and move it to a safe, fire-resistant area.
Recommended actions:
1. Disconnect the power source or load immediately
Do not attempt to “see if it recovers.”
2. Move the battery to a non-flammable area
Place it on concrete, metal, or inside a fireproof battery bag.
3. Do NOT recharge the battery
Recharging a short-circuited battery can cause thermal runaway.
4. Allow the battery to cool naturally
Never cool it with water (unless for fire suppression by professionals).
5. Dispose of the battery properly
Treat it as damaged and follow local lithium battery recycling regulations.
🚫 Never attempt to repair an internally shorted lithium battery.
Internal damage is irreversible and unsafe.
Part 6. Can improper use cause a lithium battery short circuit?
Improper use is one of the most common causes of lithium battery short circuits.
Typical misuse scenarios include:
Direct contact between positive and negative terminals
Using metal tools, loose wires, or uninsulated connectors.
Overcharging or over-discharging
Leads to lithium plating or internal separator damage.
Mechanical damage
Dropping, puncturing, or crushing the battery can cause internal shorts.
Using incompatible chargers
Incorrect voltage or current stresses internal components.
Operating outside the rated temperature range
High heat accelerates separator degradation.
In many real-world cases, short circuits are user-induced rather than manufacturing defects.
Part 7. How to use lithium batteries correctly to prevent short circuits?
Correct usage and protection design are the most effective ways to prevent lithium battery short circuits.
Best practices include:
Use a battery with built-in protection (BMS/PCM)
Protects against short circuit, overcharge, and over-discharge.
Avoid exposing terminals
Always use insulated connectors and proper casing.
Use the correct charger
Match voltage, current, and charging protocol exactly.
Do not exceed rated current
Especially important for high-drain applications.
Store batteries properly
Cool, dry environment; partial charge (30–60%) for long-term storage.
Inspect batteries regularly
Stop using batteries that show swelling, leakage, or overheating.
Tips: 🔒 For OEM and industrial applications, custom lithium batteries with tailored protection circuits significantly reduce short-circuit risks.
Part 8. How does Ufine avoid short circuits in lithium batteries?
During the production and manufacturing process of lithium-ion batteries, excessive impurities in raw materials, unqualified manufacturing processes, and inaccurate designs related to battery safety protection will all cause substandard lithium battery quality. This increases the chance of the lithium battery exploding.
As a world-renowned lithium-ion battery manufacturer, Ufine, to prevent short circuits during the lithium battery manufacturing process, strengthens battery quality control, selects high-quality materials, and designs reasonable production processes to ensure the safety performance of batteries.
1. Electrolyte leakage
Ensure that the interior of the lithium battery is well sealed, select appropriate electrolyte components, and conduct strict quality control and testing.
2. Damage to electrode material
Ufine strengthens quality control in the lithium battery production process. Ensure the integrity and stability of electrode materials.
3. Damaged diaphragm
Ufine Battery selects high-quality separator materials and strengthens quality control during production. Ensures diaphragm integrity and stability.
4. The electrode is in contact with external metal
Ufine has always selected suitable shell materials and well-designed shell structures, strengthened quality control during the production process, and ensured the insulation performance of the battery exterior.
5. Short circuit during transportation
Ufine Battery selects appropriate packaging materials and transportation methods to strengthen protection measures while transporting lithium batteries.
Part 9. FAQs
Can a lithium battery short circuit without visible damage?
Yes. Internal short circuits can occur due to separator aging, microscopic metal debris, or manufacturing defects, even when the battery looks normal from the outside.
Is an internal short circuit more dangerous than an external short circuit?
Generally, yes. Internal short circuits are harder to detect and can lead to delayed thermal runaway, while external short circuits are usually cut off quickly by protection circuits.
Can a battery recover after a short circuit event?
No. Once a lithium battery experiences a short circuit, its internal structure is permanently damaged, even if it appears to function temporarily afterward.
Does a higher-capacity lithium battery increase short circuit risk?
Not inherently. Capacity alone does not increase risk, but higher-capacity batteries store more energy, which can make short-circuit consequences more severe if protection is inadequate.
Can cold temperatures cause lithium battery short circuits?
Indirectly, yes. Extremely low temperatures can promote lithium plating during charging, which may later pierce the separator and cause internal short circuits.
Are protected lithium batteries completely immune to short circuits?
No. Protection circuits greatly reduce risk but cannot prevent internal short circuits caused by severe mechanical damage or internal material failure.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Battery Load Test: A Comprehensive Guide
Step-by-step battery load test guide for car, solar & industrial use. Learn how to load test a battery, interpret voltage charts, and avoid common mistakes.
The Comprehensive Guide to Battery Balancing and Battery Balancer
Discover how battery balancers improve lithium battery performance, lifespan, and safety. Learn types, functions, and tips to choose the right balancer.
What Is the Best Voltage for a Chainsaw Battery?
Compare 12V-80V chainsaw batteries for light pruning, medium firewood, and professional cutting. See best battery chainsaw with runtime charts and safety tips.
Lithium VS. Alkaline Batteries: A Comprehensive Comparison
Lithium batteries last 3–7× longer than alkaline and perform better in cold weather. Compare lifespan, cost, safety, and best uses to choose the right battery.
Comparing Lithium-Sulfur and Lithium-Ion Batteries: Which is Right for You?
Compare lithium-sulfur (Li-S) and lithium-ion batteries on energy, lifespan, cost, safety, and applications. Best choice for drones, EVs, and electronics.