The minimum operating temperature for LiPo batteries is critical for their performance and longevity. In this article, we delve into the factors influencing LiPo battery operation in cold conditions and explore best practices for charging and maintenance.
Operating Temperature of Lithium Batteries
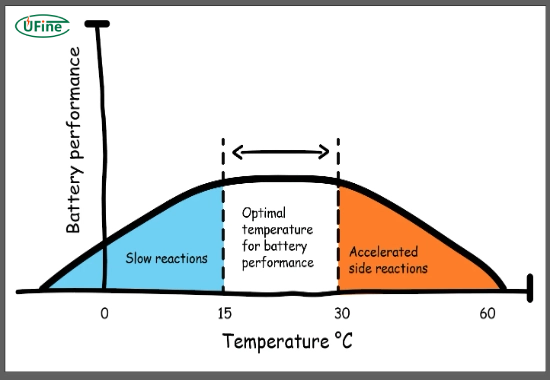
Lithium batteries, including Lithium-ion (Li-ion) and Lithium Polymer (LiPo) types, operate best within specific temperature ranges. The typical operating temperature for lithium batteries is:
- Discharge Temperature: -20°C to 60°C (-4°F to 140°F)
- Charging Temperature: 0°C to 45°C (32°F to 113°F)
- Storage Temperature: -20°C to 25°C (-4°F to 77°F) for long-term stability
Extreme cold or heat can negatively affect lithium battery performance. The table below summarizes the impact of different temperatures:
| Temperature Range | Effect on Lithium Batteries |
|---|---|
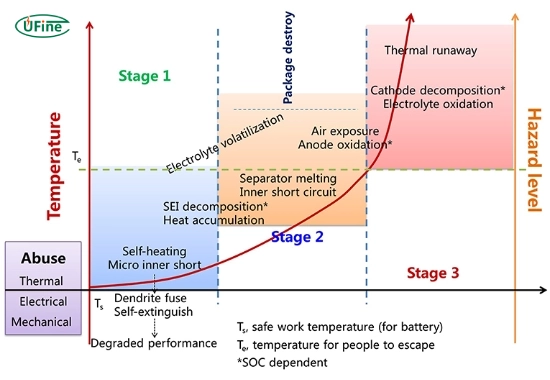
| Above 60°C (140°F) | Risk of thermal runaway, swelling, or explosion. |
| 0°C to 45°C (32°F to 113°F) | Safe charging range for most lithium batteries. |
| -20°C to 0°C (-4°F to 32°F) | Capacity loss, increased internal resistance, reduced discharge rate. |
| Below -20°C (-4°F) | Severe performance drop, possible electrolyte freezing, risk of permanent damage. |
Part 1. Minimum operating temperature for lithium batteries
The minimum operating temperature for lithium batteries varies by type. In general:
- Li-ion Batteries: Typically -20°C (-4°F) but may struggle below this range.
- LiPo Batteries: Generally between -10°C to -20°C (14°F to -4°F).
- LiFePO4 Batteries: Can function as low as -30°C (-22°F) with proper preheating.
Cold weather impacts lithium batteries by reducing ion mobility and increasing internal resistance, leading to lower capacity and voltage drops. Proper insulation and temperature management are essential for reliable performance.
Artikel Terkait: What’s the Good Battery For Cold Weather?
Part 2. Factors affecting the minimum operating temperature of Li-ion batteries
Chemical Composition
- The chemical composition of LiPo batteries plays a pivotal role in their performance at low temperatures.
- Electrolytes within LiPo batteries are typically composed of lithium salts dissolved in organic solvents, and variations in these components can impact the battery’s ability to function in cold conditions.
- Electrodes, usually made of materials like lithium cobalt oxide or lithium iron phosphate, also contribute to temperature sensitivity. Changes in their properties at low temperatures can affect the battery’s discharge characteristics.
- Other materials, such as the separator between electrodes, influence ion transport and can become less effective in colder environments, impacting the battery’s overall performance.
Cell Design and Construction
- The design and construction of LiPo batteries are critical factors in determining their minimum operating temperature.
- Cell geometry, including electrode surface area and distance between electrodes, affects the battery’s ability to maintain performance in cold temperatures.
- Electrode thickness is another crucial consideration. Thicker electrodes can offer better conductivity at lower temperatures, enhancing the battery’s ability to deliver power.
- Separator materials, which physically separate the electrodes while allowing ion transport, must be carefully chosen to withstand cold temperatures without compromising performance.
- Additionally, the overall construction of the battery, such as the arrangement of cells within the pack and the enclosure design, can impact thermal management and, consequently, the minimum operating temperature of the battery system.
Part 3. How does temperature affect lithium battery performance?
Reduced Ion Mobility
- Low temperatures slow down the movement of lithium ions within the battery electrolyte, hindering ion conductivity.
- Sluggish ion mobility reduces the battery’s ability to maintain high discharge rates, impacting its overall performance.
Increased Internal Resistance
- Cold temperatures cause the materials inside the battery to become less conductive.
- Higher internal resistance impedes the flow of electrons, leading to voltage drops and reduced power output.
Voltage Depression During Discharge
- At low temperatures, lithium batteries may experience voltage depression during high-current discharges.
- This phenomenon occurs due to increased internal resistance, resulting in a temporary drop in voltage output.
Capacity Loss
- Cold temperatures diminish the efficiency of electrochemical reactions within the battery.
- Reduced reaction efficiency decreases usable capacity, limiting the battery’s energy storage and delivery capabilities.
Risk of Damage
- Exposure to extreme cold can damage lithium batteries.
- Freezing temperatures may cause electrolyte freezing, leading to internal damage or leakage, compromising battery safety and performance.
Charging Challenges
- Charging lithium batteries in cold temperatures presents challenges.
- Slower chemical reactions at low temperatures prolong charging times and may require adjustments to charging protocols to prevent overcharging or undercharging.
Effect on Discharge Rate
- Low temperatures significantly impact the discharge rate of lithium batteries, causing slower discharge rates compared to optimal operating temperatures.
Part 4. How do you charge lithium batteries in cold weather?
Temperature Monitoring
- Monitor the ambient temperature during charging to ensure it remains within the recommended range for charging lithium batteries, typically between 0°C to 45°C (32°F to 113°F).
- Use a thermometer or temperature sensor to measure the battery’s temperature and surroundings accurately.
Preconditioning
- Precondition the battery by warming it up to a suitable temperature before charging.
- Avoid charging extremely cold lithium batteries, as this can lead to decreased charging efficiency and potential damage to the battery.
Use a Battery Warmer
- Utilize battery warmers or insulated charging bags to maintain the battery’s temperature during charging.
- These accessories help prevent the battery from getting too cold and ensure more efficient charging.
Slow Charging
- Opt for slower charging rates when charging lithium batteries in cold weather.
- Slower charging helps mitigate the impact of low temperatures on the battery’s chemical reactions. It reduces the risk of overcharging or overheating.
Avoid Rapid Charging
- Avoid rapid charging or fast charging modes in cold weather conditions.
- Rapid charging can generate excess heat, which may not dissipate effectively in cold temperatures, leading to battery damage or reduced lifespan.
Monitor Charging Progress
- Regularly check the battery’s temperature and charging progress during the charging process.
- If the battery starts to heat up excessively, stop charging immediately and allow it to cool down before resuming charging.
Charge Indoors
- Charge lithium batteries indoors or in a sheltered environment to minimize exposure to cold temperatures.
- Charging indoors helps maintain a more stable and warmer environment for the battery.
Use Battery Management Systems (BMS)
- Employ battery management systems that include temperature monitoring and protection features.
- BMS systems can help regulate charging parameters based on temperature conditions, ensuring safe and efficient charging in cold weather.
Part 5. FAQs
-
What is the best battery for low temperatures?
The best battery for low temperatures is the lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) battery because it performs well even in icy conditions. -
What batteries are very cold?
LiFePO4 batteries are suitable for frigid temperatures because they maintain their performance and capacity even in extreme cold. -
Are batteries affected by low temperatures?
Yes, batteries can be affected by low temperatures. Some types may lose capacity or need help to deliver power efficiently in cold conditions. -
Do lithium batteries work in extreme cold?
Yes, lithium batteries can work in extreme cold. Still, their performance may decrease and not function optimally compared to warmer temperatures. -
What is the low-temperature cutoff for LiFePO4?
The low temperature cutoff for LiFePO4 batteries is typically around -20 °C to -30 °C (- 4°F to- 22°F). Below this temperature, their performance may decline significantly. -
What is the ideal lithium battery operating temperature?
The ideal operating temperature for lithium batteries is between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). At this range, lithium-ion and lithium-polymer batteries maintain optimal performance, lifespan, and safety. -
What happens if a lithium battery gets too cold?
When lithium batteries are exposed to extreme cold, they experience higher internal resistance, lower voltage, and reduced capacity. If temperatures drop below -20°C (-4°F), some lithium batteries may fail to operate. -
How do you keep lithium batteries warm in winter?
To keep lithium batteries warm in cold weather, use insulated battery covers, store them indoors, and preheat them before use if necessary.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Paper Battery vs. Flexible Battery: What’s the Difference and Which Is Better?
Paper vs. flexible batteries: learn the key differences, benefits, and which power source fits best for wearables, sensors, and smart tech.
What to Know Before Buying a Tiny LiPo Battery for Your Project
Tiny LiPo batteries are powerful and compact. Learn how to choose the right one for your project with specs, safety, and charging tips.
Bloated LiPo Battery: Will It Explode?
Will a bloated LiPo battery explode? Discover the causes, risks, safety steps, and expert tips to avoid disaster and protect your gear. Must-read safety guide!
12V 100Ah Lithium Ion Battery Price: Full Guide
Learn about 12V 100Ah lithium-ion battery price, from cost ranges to best brands, hidden fees, and how to get the best deal. A must-read for smart buyers!
Resistance and Conductivity: What It Means for Your Lithium Batteries
Resistance and conductivity impact lithium battery performance, lifespan, and safety—learn how they work and why they matter.