When it comes to understanding the voltage of an AC battery, many people find themselves puzzled. After all, the concept of an “AC battery” can seem contradictory at first glance. Batteries are traditionally known for providing direct current (DC) while alternating current (AC) is typically associated with power from the grid or generators. So, what exactly is the voltage of an AC battery, and how does it function? This article breaks down the basics, clarifies common misconceptions, and explores how AC batteries work in practical applications.
This guide will help you understand AC battery voltage, its operation, and its role in modern technology.
Part 1. What is an AC battery?
An AC battery is not a traditional battery in the conventional sense. Instead, it refers to an energy storage system that integrates a battery (usually DC-based) with an inverter. The inverter converts the DC power stored in the battery into AC power, which can power household appliances, industrial equipment, or other devices that require alternating current.
In simpler terms, an AC battery combines a battery and an inverter to deliver AC power directly. This makes it particularly useful in renewable energy systems, such as solar power setups, where stored energy must be converted from DC to AC before use.
Part 2. What is the voltage of an AC battery?
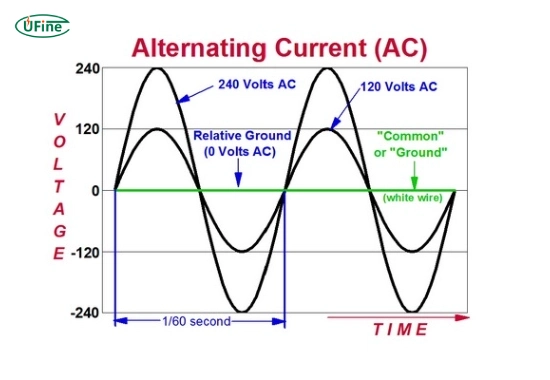
The inverter inside an AC battery determines its voltage. Typically, the inverter outputs a standard AC voltage of 120V or 240V (depending on the region), compatible with the electrical systems used in homes and businesses.
However, the actual voltage of the battery inside the AC battery system is in DC form and often ranges between 12V, 24V, or 48V, depending on the battery’s design and capacity.
So, to summarize:
- An AC battery usually outputs 120V or 240V AC, depending on its use location.
- The battery’s internal voltage (in DC form) is typically 12V, 24V, or 48V.
Part 3. How does an AC battery work?
An AC battery operates by combining two key components:
- The battery is the energy storage unit that stores electricity through direct current (DC). Common battery types include lithium-ion, lead-acid, or other advanced chemistries.
- The inverter converts the stored DC power into AC power, which standard electrical devices can use.
When energy is needed, the inverter takes the DC electricity from the battery, processes it, and delivers it as AC power at the required voltage and frequency. This seamless conversion process is what makes AC batteries so versatile and user-friendly.
Part 4. What are the applications of AC batteries?
People use AC batteries in various applications because of their high versatility, including:
- Renewable energy systems: AC batteries are commonly used in solar and wind power installations to store excess energy and supply it in AC form when needed.
- Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS): These systems rely on AC batteries to provide backup power during outages.
- Portable energy solutions: Many portable power stations and generators use AC battery systems to power appliances, tools, and devices on the go.
- Electric vehicles (EVs): EV batteries are primarily DC-based, but some advanced systems incorporate AC components for specific functionalities.
Part 5. What are the advantages of AC batteries?
AC batteries offer several key benefits:
- Ease of use: The built-in inverter provides plug-and-play functionality for delivering AC power directly.
- Compatibility: The AC output makes them compatible with most household and commercial appliances.
- Versatility: You can use AC batteries in both on-grid and off-grid systems.
- Energy efficiency: Modern AC battery systems have minimal energy loss during the DC-to-AC conversion process.
- Compact design: Combining the battery and inverter in one unit saves space and simplifies installation.
Part 6. How does the voltage of an AC battery vary?
The inverter’s design and the region’s electrical standards typically fix an AC battery’s output voltage at 120V or 240V.
For example:
- Small systems: Use batteries with 12V or 24V DC.
- Larger systems: Use 48V DC or higher batteries for greater storage capacity and efficiency.
The inverter ensures that the output remains consistent, regardless of the internal battery voltage.
Part 7. Can AC batteries charge with AC power?
Yes, AC batteries can charge using AC power. The inverter in an AC battery system often functions as a bidirectional inverter. It can also convert AC power from the grid or another source into DC to charge the battery. This capability makes AC batteries highly flexible for both storing and delivering energy.
Part 8. What factors influence the performance of AC batteries?
Several factors affect the performance and efficiency of AC batteries:
- Battery type: Lithium-ion batteries are more efficient and longer-lasting than lead-acid batteries.
- Inverter quality: A high-quality inverter ensures minimal energy loss during the DC-to-AC conversion process.
- Temperature: Extreme temperatures can affect battery performance and lifespan.
- Load requirements: The energy demand of connected devices determines how long the AC battery can supply power.
Part 9. What is the difference between an AC battery and a DC battery?
The primary difference between an AC battery and a DC battery lies in their output:
- AC battery: Outputs alternating current (AC) directly, making it compatible with most appliances.
- DC battery: Direct current (DC) is output, requiring users to connect an external inverter to use AC appliances.
An AC battery includes a built-in inverter, while a DC battery does not.
Part 10. Are AC batteries the future of energy storage?
With the growing adoption of renewable energy systems and the need for efficient energy storage, AC batteries are becoming increasingly popular. Their ability to deliver AC power directly makes them user-friendly and ideal for residential and commercial applications. As battery technology advances, we can expect AC batteries to play an even more significant role in the energy landscape.
Part 11. FAQs
-
What voltage does an AC battery output?
AC batteries typically output a standard AC voltage of 120V or 240V, depending on the region. The internal battery voltage (in DC form) is often 12V, 24V, or 48V. -
Can I use an AC battery with solar panels?
Yes, AC batteries are commonly used in solar energy systems. They store excess energy generated by the solar panels and deliver it as AC power when needed. -
How long does an AC battery last?
The lifespan of an AC battery depends on the battery type and usage patterns. Lithium-ion AC batteries typically last 10-15 years or 3000-5000 charge cycles. -
Can I charge an AC battery with a generator?
Yes, you can charge most AC batteries using a generator. The inverter in the AC battery system converts the generator’s AC power into DC to charge the battery. -
Are AC batteries expensive?
The cost of an AC battery system depends on its capacity, quality, and features. While they may have a higher upfront cost than standalone DC batteries, their convenience and efficiency often make them a worthwhile investment.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Best Jigsaw Tool Battery for Long-Lasting Power
Discover the top jigsaw tool batteries for power & runtime. Compare Li-ion vs. NiCd, top brands, and tips to extend battery life. Read now
The Logistics of Bulk Battery Orders: Shipping, Storage, and Hazmat Compliance
Learn how to safely manage bulk battery orders with tips on shipping, storage, and hazmat compliance for smarter, safer logistics.
Microcurrent Facial Device Battery Guide & Tips
Learn all about microcurrent facial device batteries, from types to lifespan, and how to choose a reliable supplier for long-lasting, safe skincare performance.
Power Pack Battery vs. Power Bank: What’s the Difference?
Power pack vs power bank: Learn the key differences, pros, and best uses to choose the right portable power source for your lifestyle.
What Is a Power Pack Battery and How Does It Work?
A power pack battery stores energy for off-grid use, emergencies, or travel. Learn how it works and how to choose the right one for your needs.