What is UN38.3? UN38.3 testing plays a vital role in ensuring the safety and compliance of battery-powered products. This article explores the significance of UN38.3 testing, its classification, procedures, and why it’s essential for product safety and compliance.
Part 1. What is UN38.3?
UN38.3 refers to the United Nations Manual of Tests and Criteria, Part III, Section 38.3, a comprehensive safety standard for lithium-ion batteries, ensuring they meet essential criteria for safe transportation. The tests assess the batteries’ performance under extreme conditions, such as mechanical impacts, temperature fluctuations, and electrical overloads. These tests are designed to simulate potential hazards during transportation, including potential short circuits, fire risks, and thermal runaway incidents. Compliance with UN38.3 is essential not only for regulatory approval but also for minimizing environmental and human health risks during battery transport.
What is Battery Cell Thermal Runaway?
Part 2. UN 38.3 classification
UN 38.3 classification categorizes lithium-ion batteries based on their type or mode of transportation, ensuring adherence to safety and compliance standards. Here are the key classifications:
By Battery Type
- Lithium Metal Batteries (UN 3090): These batteries are typically used in consumer products such as watches and cameras, as well as in industrial applications. Because lithium metal is highly reactive, these batteries are subject to stringent testing requirements to minimize risks of leakage, short circuits, or fires during transit.
- Lithium Ion Batteries (UN 3480): Widely used in electronics like smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles, lithium-ion batteries store energy using lithium ions. They require rigorous testing to ensure that they can withstand environmental stresses, such as temperature fluctuations or mechanical damage, without posing a hazard during transport.
- Lithium Ion Batteries Contained in Equipment (UN 3481): Often found in devices such as medical equipment, these batteries are transported within the device itself. Despite being less prone to immediate hazards, these batteries still require compliance with UN38.3 standards to ensure safe handling and prevent accidents.
By Transportation Mode
- Ground Transportation (UN38.3.1): Batteries destined for road or rail transport must pass rigorous safety tests to ensure that packaging and labeling meet international safety standards. This includes evaluations of battery stability under vibrations, impacts, and temperature extremes that may occur during road transit.
- Air Transportation (UN38.3.2): Air transport of lithium-ion batteries is one of the most regulated areas due to the increased risk of fire, explosion, or chemical leakage in high-pressure, low-oxygen environments. UN38.3 testing for air transportation includes specific tests to ensure that the batteries will not overheat or cause other hazards under high-altitude conditions.
- Sea Transportation (UN38.3.3): Sea transport is the most common method for international shipping, but it also poses unique risks. UN38.3 testing ensures that lithium-ion batteries transported by sea meet safety standards to prevent risks like fire or leakage, which could cause severe environmental damage or contamination.
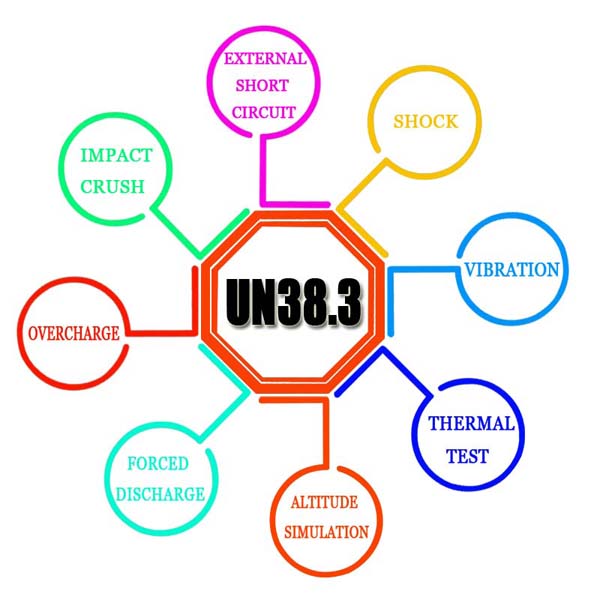
Part 3. Key UN38.3 testing procedures for lithium-ion batteries
UN38.3 testing procedures encompass a series of rigorous assessments to ensure the safety and compliance of lithium-ion batteries. Here are the key steps :
- Mechanical Shock Test: This test simulates the impact of drops or collisions that can occur during transport. The battery is subjected to a mechanical shock to check if it is structurally sound and able to withstand external pressure or hits. Any damage to the casing or battery internals could result in dangerous situations such as short circuits or thermal runaway.
- Thermal Test: Lithium-ion batteries are sensitive to temperature extremes. This test involves subjecting the battery to both high and low temperatures to simulate environments in which the battery may be exposed. The goal is to evaluate how the battery responds to these extremes, ensuring it does not leak, rupture, or catch fire.
- Vibration Test: During transport, batteries often encounter vibrations due to vehicle movement. This test assesses whether the battery can endure mechanical vibrations without experiencing failure, which could result in leakage or other hazards. The test is designed to simulate the kind of shaking a battery would endure during road, rail, or sea transport.
- Overcharge Test: The overcharge test examines the battery’s response when it is charged beyond its rated capacity. This can occur due to faulty charging equipment or other mishaps. The test ensures that the battery can safely handle overcharging without causing hazardous reactions like leakage, fire, or explosion.
- Altitude Simulation Test: For air transport, it is essential to test the battery’s response to changes in atmospheric pressure. This test simulates the high altitudes experienced during air travel to ensure the battery can withstand the pressure changes without leaking or failing.
Part 4. Why is UN38.3 testing necessary?
Ensuring Safety
UN38.3 testing is critical for ensuring lithium-ion battery safety during transport. By subjecting batteries to tests like thermal runaway prevention, potential hazards such as fires or explosions are mitigated. This ensures that batteries remain safe under various conditions, including transport by air, sea, or ground.
Compliance with Regulations
Many countries and international organizations require compliance with UN38.3 testing standards for transporting lithium-ion batteries. Adhering to these regulations is essential for businesses to avoid legal consequences, fines, or product recalls resulting from non-compliance.
Protecting the Environment
Proper testing and certification of lithium-ion batteries help prevent environmental damage caused by battery-related incidents such as fires or leaks. Ensuring batteries meet UN38.3 standards significantly reduces the risk of environmental contamination from hazardous materials.
Building Consumer Trust
Consumers expect the products they purchase to be safe and reliable. UN38.3 testing provides a standardized method for assessing battery safety. It guarantees consumers that their products have undergone thorough testing and meet established safety standards.
Preventing Accidents during Transportation
Lithium-ion batteries pose unique risks during transportation due to their chemical composition and energy density. UN38.3 testing helps identify potential hazards and ensures batteries are packaged and handled safely to prevent accidents such as fires or explosions during transit.
Reducing Liability Risks
Non-compliance with safety regulations can expose businesses to liability risks in the event of accidents or injuries caused by unsafe products. UN38.3 testing helps mitigate these risks by identifying and addressing potential safety hazards before products reach the market.
Part 5. Industry case studies: Importance of UN38.3 testing in the real world
Several high-profile incidents have demonstrated the importance of UN38.3 compliance for lithium-ion batteries. For example, the well-known recall of Samsung Galaxy Note 7 smartphones was due to battery defects that caused overheating and fires. This incident underscores the importance of strict adherence to safety standards, including UN38.3 testing, to ensure the safe transport and use of lithium-ion batteries. Companies in the electric vehicle industry also face similar risks, as faulty batteries in electric cars can result in fires or other catastrophic failures if they aren’t properly tested for transportation.
Part 6. FAQs
-
Is UN38.3 mandatory?
Yes, UN38.3 is mandatory for transporting lithium-ion batteries safely worldwide. -
How long does UN38.3 testing take?
Testing typically takes several weeks, depending on the complexity of the battery and testing requirements. -
What is the difference between MSDS and UN38.3?
MSDS provides safety data for materials, while UN38.3 focuses on the safety of lithium-ion batteries during transport. -
What is the purpose of UN38.3?
UN38.3 ensures lithium-ion battery safety during transportation, reducing risks such as fires and explosions. -
What is the difference between UN38.3 and IEC62133?
UN38.3 covers transportation safety, while IEC 62133 focuses on battery safety standards.
Related Tags:
More Articles

Learn what UL1642 certification is, how the UL1642 standard tests lithium battery cells, and how it differs from UL2054. UL1642 battery safety guide.
LMFP Battery Market Outlook: Will It Replace LFP and NMC?
Explore LMFP battery performance, LMFP vs LFP and LMFP vs NMC comparisons, energy density, cost, safety, and 2026 market outlook for EV and ESS applications.
리튬이온배터리 사용 중 돌출부가 생겼을 때 안전하게 관리하고 사고를 예방하는 방법, 부풀음 발생 원인과 예방 팁을 알려드립니다.
Stack Battery vs Winding Battery: Structural, Performance & Application Comparison
Compare stack battery and winding battery structures, energy density, cost, and applications in EV, ESS, and custom lithium battery design.
Why Is My Lithium Battery Bulging? Safety Tips Inside
Learn how to spot a swollen battery, prevent damage, and stay safe. Don’t wait until it’s too late!