BYD’s Blade Battery belongs to the category of lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries. Its unique design, resembling a long, flat blade, is where it gets its name.
Some consumers may have heard claims like “longer range” or “faster charging” associated with the Blade Battery. However, BYD’s official marketing doesn’t emphasize these features. Instead, the focus is on safety—BYD states that safety is the ultimate luxury for electric vehicles.
Part 1. The birth of the blade battery
The Blade Battery is an optimized and evolved version of the traditional lithium iron phosphate battery. By reimagining the shape and design of the cells, BYD has created a product that stands out in both appearance and functionality. Previously, this type of battery was referred to as the “Super Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery” within the industry. Adopting the “Blade Battery” name adds a sense of imagination and visual impact.
BYD has consistently adhered to using lithium iron phosphate as the cathode material for its batteries because of its significant safety advantages over ternary lithium batteries.
Differences Between LFP and Ternary Batteries:
- LFP Batteries: Known for greater safety, making them less likely to overheat or catch fire.
- Ternary Batteries: Offer higher energy density, resulting in longer range due to superior conductivity and energy storage capabilities.
BYD’s founder, Wang Chuanfu, has long criticized the pursuit of range at the expense of safety. However, it’s worth noting that BYD doesn’t entirely reject ternary batteries—they are still used in some models. Striking a balance between long range and safety remains a crucial direction for future development.
The Blade Battery represents the best of both worlds, combining the safety of LFP with advancements that enhance energy density, making it an optimal solution for modern electric vehicles.
BYD Blade Battery Comprehensive Guide
Part 2. Structural design of the blade battery
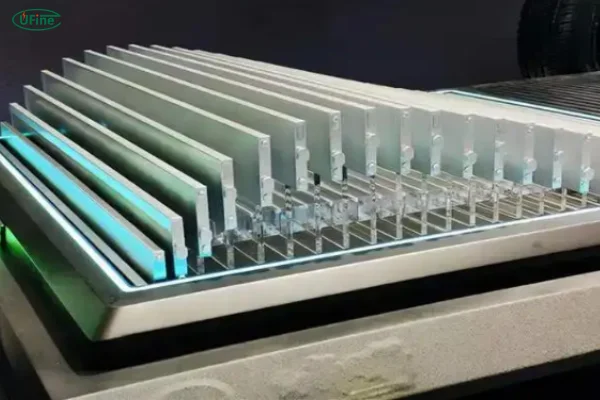
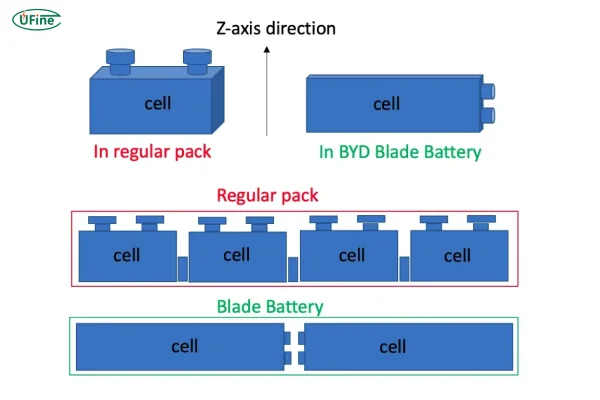
The Blade Battery adopts a structural design inspired by its namesake—long and thin like a blade. Its construction differs significantly from traditional battery packs:
Key Design Innovations:
-
Thin and Flat Cells:
Traditional battery packs consist of multiple block-like or cylindrical cells. In contrast, the Blade Battery uses elongated and flat cells that are densely arranged. -
Space Optimization:
- Traditional block-shaped batteries have a space utilization rate of only about 40% due to support structures and cooling components.
- The Blade Battery eliminates these inefficiencies by designing the battery cells themselves as structural supports, achieving a space utilization rate of around 60%.
-
Energy Density Improvement:
This efficient design allows for more cells to be packed into the same volume, thereby increasing energy density and enabling longer driving ranges.
BYD refers to this as a module-free design or CTP (cell-to-pack) technology. By integrating LFP cells in sizes ranging from 600mm to 2,500mm, the Blade Battery achieves a high level of efficiency and compactness, optimizing the structure of the battery pack.
Part 3. Does the blade battery offer longer range or faster charging?

The Reality Behind the Claims:
From a technical standpoint, the Blade Battery doesn’t inherently provide “longer range” or “faster charging.”
-
Range:
- The driving range of an electric vehicle depends on the total capacity of the battery pack, not its type. An 80kWh battery, whether LFP or ternary, provides the same range.
-
Charging Speed:
- Compared to ternary batteries, LFP batteries have a lower maximum charge and discharge power, meaning their theoretical charging speed is slightly slower.
Practical Advantages:
However, practical use cases reveal some scenarios where the Blade Battery does appear to excel:
-
Longer Usable Range:
LFP batteries can be charged to 100% daily without significant degradation, unlike ternary batteries that are typically charged to only 90%. Over time, this translates to more usable range in real-world conditions. -
Faster Charging Under Specific Conditions:
At older charging stations with lower maximum currents (e.g., 120A), the BYD Han equipped with a 600V system charges faster than many other EVs, as it can achieve higher power levels.
Part 4. Is the blade battery safer?
Inherent Safety of LFP Batteries:
Lithium iron phosphate batteries are inherently safer than ternary batteries due to their:
- Higher Thermal Stability: They are less likely to undergo thermal runaway, a chain reaction of overheating.
- Lower Heat Release During Reactions: The materials used in LFP batteries release less heat during chemical reactions, reducing the risk of fires or explosions.
BYD’s Contributions to Safety:
While safety is an intrinsic feature of LFP batteries, BYD has enhanced it further by:
- Passing rigorous safety tests, including nail penetration tests, which simulate extreme conditions.
- Developing an integrated battery pack design that optimizes heat dissipation and structural integrity.
Part 5. The blade battery’s impact on the industry
Advantages Over Other Batteries:
- Energy Density: By improving the cell-to-pack efficiency, the Blade Battery achieves higher energy density compared to traditional LFP batteries, enabling ranges of 600-700km.
- Affordability: LFP batteries are more cost-effective than ternary batteries, making EVs more accessible.
- Safety Leadership: BYD’s advancements have set a new standard, encouraging broader adoption of LFP batteries in the EV industry.
However, consumers should understand that overall EV performance depends not only on the battery but also on the automaker’s system integration and design capabilities.
Part 6. Summary—what does the blade battery mean for consumers?
For everyday users, the Blade Battery offers:
- Enhanced Safety: A more stable and reliable battery system.
- Usable Range: Daily charging to 100% without degradation translates to more range in practical use.
- Improved Charging Speeds: Faster charging at older charging stations due to higher voltage platforms.
At the industry level, the Blade Battery represents a significant step forward, showcasing how innovation can make LFP batteries more competitive, safer, and practical for a broader range of EV applications.
In conclusion, while the Blade Battery may not revolutionize EVs in terms of range or charging speed, its safety, efficiency, and design innovations have cemented its position as a cornerstone of BYD’s EV strategy.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Best Floor Scrubber Battery for Commercial Cleaning?
Selecting the ideal floor scrubber battery ensures a long runtime, rapid charging, and minimal maintenance for efficient commercial cleaning operations.
Battery for Blower vs Battery for Leaf Vacuum: Which One Should You Choose?
Battery for blower vs leaf vacuum—learn the key differences in power, fit, and runtime to choose the right battery for your outdoor tool needs.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Blower?
Choosing the right blower battery? Consider voltage, capacity, chemistry & usage. This guide helps match the best battery for peak performance.
How to Choose the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries?
Choosing the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries? Discover key factors such as size, material, and safety for optimal protection and performance.
7 Critical Elements on a Lithium Battery Shipping Label
What must be on a lithium battery shipping label? Learn 7 key elements to ensure safety, legal compliance, and correct handling across all transport modes.