Cylindrical batteries are integral to modern electronic devices, providing reliable energy storage and release. This guide explores their structure, variations, and specific types like the 21700, 26650, 14500, and 16650 batteries.
Part 1. Understanding the structure of a cylindrical battery
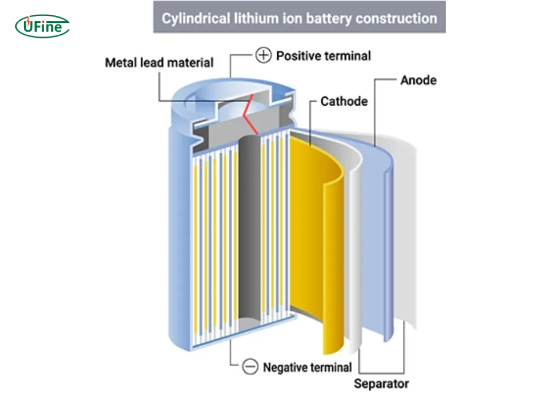
The cylindrical battery, a staple in electronic devices, possesses a defined structure crucial to its functionality. Typically encased in a cylindrical shell, these batteries feature an internal configuration that facilitates energy storage and release.
Core Components of Cylindrical Batteries
Anode and Cathode
At the structure’s core lie the anode and cathode, constructed with specific materials conducive to electron flow during the battery’s charging and discharging cycles.
Separator
The separator is a barrier, often a microporous polyethylene or ceramic film. It prevents direct contact between the anode and cathode, facilitating the movement of ions while preventing short circuits. This crucial element ensures the prevention of short circuits, maintaining the battery’s stability and safety.
Electrolyte Solution
The internal space of the battery contains an electrolyte solution that facilitates the movement of ions between the anode and cathode during the energy transfer process. This solution is pivotal in the battery’s overall performance and efficiency.
Casing
The outer cylindrical casing, usually composed of metal or other durable materials, safeguards the internal components. It not only provides structural support but also serves as a protective shield against external impacts and environmental factors.
Variations in Cylindrical Battery Structure
Different cylindrical batteries may exhibit variations in internal components and casing materials based on their intended applications. High-capacity batteries designed for heavy-duty applications might incorporate thicker electrodes or more advanced separator materials to enhance performance and longevity.
Part 2. 21700 Cylindrical battery: A high-energy solution
The 21700 battery is more significant than the 18650, being 21mm wide and around 70mm long. It can store more energy, making it suitable for things that need much power for a long time. It usually has 3.6 to 3.7 volts and can hold between 4000mAh to 5000mAh. This makes it great for things that need much power for a long time.
Pros and Cons of 21700 Battery
Pros:
- Enhanced Energy Density: The 21700 battery exhibits higher energy density than its smaller counterparts, allowing more excellent energy storage within the same physical space. This increased density contributes to improved performance and longer usage durations in devices.
- Increased Capacity: With its larger size, the 21700 battery offers greater capacity, enabling devices to charge more. This feature is particularly beneficial for high-power applications, providing sustained performance over extended periods.
- Improved Performance: Lower internal resistance within the 21700 battery enhances energy transfer efficiency, resulting in superior performance and higher discharge rates. This characteristic makes it suitable for high-drain applications that demand consistent power output.
Cons:
- Cost Considerations: The production costs of 21700 batteries can be higher than smaller cells due to the larger quantities of materials required. This factor may impact their adoption of devices where cost-efficiency is crucial.
- Compatibility Challenges: Some devices may not accommodate the larger size of the 21700 battery, requiring modifications or redesigns for integration. This limitation can restrict its use in certain products.
21700 Battery Applications
Electric Vehicles (EVs)
The 21700 battery’s superior energy density and increased capacity make it a preferred choice in the automotive industry, especially in electric vehicles. Its ability to store more energy allows EVs to achieve longer driving ranges, contributing to the widespread adoption of this battery type in the EV sector.
Renewable Energy Storage Systems
In renewable energy applications like solar power units and home energy storage systems, the 21700 battery’s efficiency in storing substantial amounts of energy makes it a valuable component. These batteries ensure a consistent power supply by efficiently keeping surplus energy generated from renewable sources for later use.
High-Performance Devices
The 21700 battery utilizes high-performance devices such as power tools, professional-grade flashlights, and portable electronics. Its increased capacity and improved performance cater to devices requiring sustained high power output and extended usage durations.
Part 3. 26650 Cylindrical battery: power and durability
The 26650 battery is larger than the 18650, with a diameter of about 26mm and a length of around 65mm. This bigger size allows it to store more energy, making it suitable for devices that need prolonged usage and high power outputs. It usually has a voltage of 3.6 to 3.7 volts and can hold between 4000mAh and 5500mAh, showing its ability to store a lot of charge in its larger size.
Pros and Cons of 26650 Battery
Pros:
- Enhanced Capacity: The 26650 battery offers a larger capacity than smaller cells, enabling devices to charge more—this increased capacity benefits applications requiring sustained power supply over extended periods.
- Greater Energy Density: With its more prominent form factor, the 26650 battery can store more energy within the same physical space. This heightened energy density improves performance and efficiency in powering high-drain devices.
- Improved Durability: The larger size of the 26650 battery often translates to increased durability, making it more resilient to physical stressors and providing longer operational lifespans.
Cons:
- Size and Weight: The larger size and weight of the 26650 battery can pose challenges for integration into devices designed for smaller cells, limiting its applicability in certain compact electronics.
- Cost Considerations: Producing the 26650 battery may incur higher costs due to the increased quantities of materials required, potentially impacting its adoption in cost-sensitive industries.
26650 Battery Applications
Energy Storage Systems
Due to its larger capacity and durability, the 26650 battery finds substantial use in renewable energy storage systems. It efficiently stores surplus energy from solar or wind power sources, ensuring consistent energy availability for homes or businesses.
High-Performance Flashlights
High-output flashlights and illumination devices benefit from the 26650 battery’s enhanced capacity and energy density. These batteries power flashlights in professional settings, providing prolonged and powerful illumination.
Power Tools and Electric Vehicles
The 26650 battery’s robust capacity and durability suit it for power tools and specific electric vehicle applications. Its ability to deliver sustained power output meets the demands of these high-drain devices, contributing to their efficient operation.
Part 4. 14500 Cylindrical battery: compact and versatile
The 14500 battery is smaller than the 18650, with a diameter of about 14mm and a length of around 50mm. It’s great for small devices with limited space. This battery usually has a voltage of 3.6 to 3.7 volts. It can hold between 600mAh and 1200mAh, making it suitable for compact applications that need a moderate power supply without taking up much space.
Pros and Cons of 14500 Battery
Pros:
- Compact Size: The 14500 battery’s smaller form factor allows easy integration into devices with limited space, making it suitable for compact gadgets and portable electronics.
- Moderate Capacity: Despite its size, the 14500 battery offers an average capacity, enabling it to store a reasonable amount of charge within its compact dimensions.
- Versatility: Its smaller size and adequate capacity make the 14500 battery versatile for various applications that prioritize space efficiency without compromising power supply.
Cons:
- Limited Capacity: Compared to larger-sized batteries, the 14500 battery has a relatively limited capacity, which may not meet the power demands of high-drain devices requiring prolonged usage.
- Lower Energy Density: The smaller size of the 14500 battery results in a lower energy density than more giant cells, impacting its ability to store as much energy within the same space.
14500 Battery Applications
Flashlights and Portable Gadgets
Due to its small size and reasonable capacity, the 14500 battery finds extensive use in compact flashlights, torches, and portable gadgets—these batteries power devices where space is critical, ensuring adequate power supply without compromising portability.
Wireless Devices
In wireless devices like remote controls, wireless keyboards, and small sensors, the 14500 battery’s compact dimensions make it an ideal power source. Its moderate capacity meets the power needs of these devices while maintaining a smaller form factor.
Emergency Lighting
Emergency lighting systems, including backup lights and emergency torches, often utilize 14500 batteries because they provide sufficient power in compact emergency devices, ensuring reliable illumination during critical situations.
Part 5. 16650 Cylindrical battery: balance and adaptability
The 16650 battery is in between the big 18650 and smaller ones. It’s about 16mm wide and 65mm long. This size balance means it can store a decent amount of charge—usually 3.6 to 3.7 volts and 1500mAh to 2500mAh. It’s a versatile choice for devices that need a good mix of power and a compact size.
Pros and Cons of 16650 Battery
Pros:
- Balanced Size: The 16650 battery offers a flat size between standard cylindrical cells and smaller options, which compromises capacity and form factor and is suitable for various devices.
- Moderate Capacity: Despite its intermediate size, the 16650 battery maintains an average capacity, enabling it to store a reasonable amount of charge within its adaptable dimensions.
- Versatility: Its mid-sized dimensions make the 16650 battery versatile for applications that prioritize a balance between power output and space efficiency, catering to devices requiring moderate power within limited space.
Cons:
- Limited Capacity: Compared to larger-sized batteries, the 16650 battery’s capacity is relatively moderate, potentially limiting its suitability for high-drain devices needing sustained usage.
- Size Constraints: In smaller gadgets or ultra-compact electronics, the 16650 battery’s intermediate size may pose integration challenges, impacting its applicability in specific devices designed for smaller cells.
16650 Battery Applications
Flashlights and Portable Electronics
The 16650 battery finds application in flashlights, portable electronics, and specific small devices where a balance between size and power output is crucial. Its moderate capacity meets the power demands of these devices without sacrificing space efficiency.
Compact Tools and Handheld Devices
In handheld tools and compact devices such as certain types of compact cameras or portable measuring instruments, the 16650 battery’s intermediate size balances power supply and device size, it is ensuring optimal performance within limited space.
Moderate-Demand Gadgets
Devices with moderate power requirements, like certain handheld gaming consoles or compact communication devices, benefit from the 16650 battery’s adaptable size and adequate capacity, providing sufficient power without compromising device portability.
Part 6. FAQs
-
What are the different types of cylindrical batteries?
Various types of cylindrical batteries exist, including lithium-ion (Li-ion), lithium polymer (LiPo), nickel-cadmium (NiCd), nickel-metal hydride (NiMH), and alkaline batteries, differing in chemistry, voltage, and application. -
Why are batteries cylindrical?
Cylindrical batteries provide efficient use of space, as their shape allows for easy stacking in a cylindrical container. This design maximizes the battery’s capacity-to-size ratio, making them versatile for various applications. -
What are the small cylinder batteries called?
Small cylindrical batteries are often referred to as button cells. These include batteries like CR2032 and LR44, commonly used in watches, calculators, and small electronic devices. -
What is the difference between cylindrical and pouch cell batteries?
Cylindrical cells have a tubular shape, while pouch cells are flexible and rectangular, enclosed in a flexible pouch. Pouch cells offer flexibility in terms of shape but may have lower energy density compared to cylindrical cells. -
What is the drawback of a cylindrical cell battery?
One drawback of cylindrical cell batteries is that they may have limitations in specific applications due to their fixed shape, making them less adaptable to some designs compared to more flexible pouch or prismatic cells.
Related Tags:
More Articles

White Stuff on Battery Terminals: A Step-by-Step Cleaning and Maintenance Guide
White stuff on battery terminals is corrosion. Learn how to clean it safely, prevent damage, and keep your battery running strong with simple steps.
Understanding How Glass Mat Batteries Work: Technology, Benefits, and Limitations
Glass mat batteries power cars, RVs, and solar systems. Learn how they work, their benefits, and what to consider before choosing one.
A Buyer’s Guide for AA Size Lithium Battery
Discover the power of AA size lithium batteries—types, voltage, capacity, and more! Learn how to choose the best one for your needs. Read now!
Li-Ion Battery Prices – Where to Buy Cheap & Safe
Discover li-ion cell prices, key market factors, and how to find affordable custom batteries from top suppliers like Ufine Battery.
How Long Does a 2200mAh Battery Last?
Discover everything about 2200mAh batteries—types, charging time, lifespan, and whether it’s enough for your device.