- Part 1. What is a zinc-air battery?
- Part 2. What are lithium-ion batteries?
- Part 3. Differences between zinc-air and lithium-ion batteries
- Part 4. Advantages of zinc-air and lithium-ion batteries
- Part 5. Disadvantages of zinc-air and lithium-ion batteries
- Part 6. Applications of zinc-air and lithium-ion batteries
- Part 7. How to choose between zinc-air and lithium-ion batteries?
- Part 8. FAQs on zinc-air vs lithium-ion batteries
Regarding energy storage solutions, zinc-air and lithium-ion batteries are two prominent technologies that often come into the discussion. Each has its unique characteristics, advantages, and applications. This article will examine the differences between these two battery types, enabling you to understand their functionalities, benefits, and potential drawbacks.
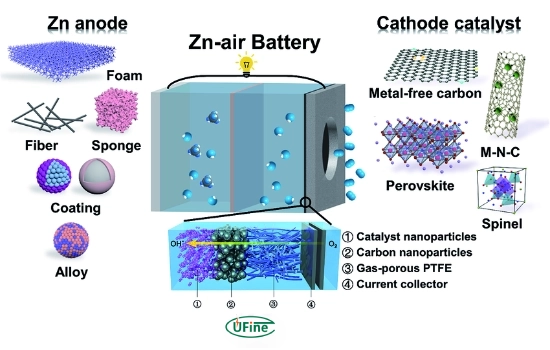
Part 1. What is a zinc-air battery?
Zinc-air batteries utilize zinc as the anode and oxygen from the air as the cathode. This type of battery is known for its high energy density, making it an attractive option for various applications, particularly in hearing aids and other small electronic devices. For an in-depth technical overview, see the IEEE paper on zinc-air battery technology, and for manufacturer specifications, visit Duracell’s zinc-air product page.
- High energy density (≈300 Wh/kg)
- Cost-effective and eco-friendly
- Ideal for low-drain, lightweight devices
Common Questions About Zinc-Air Batteries
Are zinc-air batteries rechargeable?
Most zinc-air batteries are primary cells and cannot be recharged. Research into rechargeable zinc-air systems is ongoing but not yet widely available.
What are the advantages of zinc-air batteries?
Zinc-air batteries offer high energy density, low cost, and environmental friendliness, making them ideal for hearing aids and other low-drain devices.
How long do zinc-air batteries last?
Battery life depends on discharge rate and humidity, but they typically last from several days up to a few weeks under normal conditions.
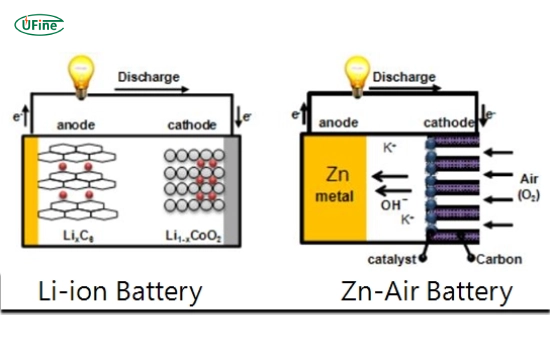
How Do Zinc Air Batteries Work?
Zinc-air batteries generate electricity through a chemical reaction between zinc and oxygen. The essential operation can be summarized as follows:
- Oxidation Reaction: Zinc is oxidized at the anode, releasing electrons.
- Reduction Reaction: Oxygen from the air is reduced at the cathode, consuming electrons.
- Ion Movement: Zinc ions move through an electrolyte to complete the circuit.
This process results in a higher energy density than many other battery types, so zinc-air batteries are often used in applications requiring lightweight and compact energy sources.
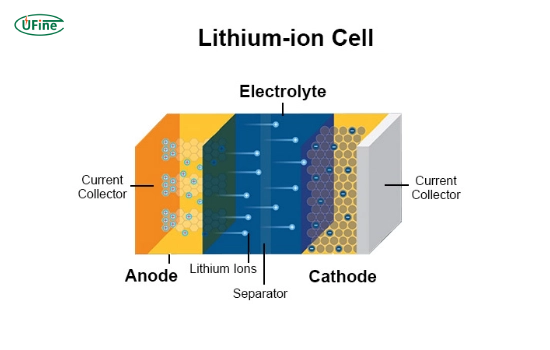
Part 2. What are lithium-ion batteries?
Lithium-ion batteries are rechargeable batteries that use lithium ions as the primary charge carrier. Due to their high efficiency and long cycle life, they are widely used in consumer electronics, electric vehicles, and renewable energy storage systems. For a government white paper, refer to the U.S. DOE battery white paper, and for a deep-dive blog analysis, see Battery University’s guide to lithium-ion chemistries.
How Do Lithium-Ion Batteries Work?
The operation of lithium-ion batteries involves the following steps:
- Lithium Ion Movement: During discharge, lithium ions move from the anode (usually made of graphite) to the cathode (often a lithium metal oxide).
- Electron Flow: As lithium ions move, electrons flow through an external circuit, providing power to devices.
- Recharging: When recharging, the process reverses, with lithium ions moving back to the anode.
People recognize lithium-ion batteries for their high energy density, low self-discharge rate, and capability to recharge hundreds of times.
Part 3. Differences between zinc-air and lithium-ion batteries
The differences between zinc-air and lithium-ion batteries can be summarized as follows:
- Energy Density: Zinc air batteries offer a higher energy density (up to 300 Wh/kg) than lithium-ion batteries (150-250 Wh/kg).
- Weight: Zinc-air batteries are lighter because they use air as a reactant, while lithium-ion batteries are heavier because of their materials.
- Rechargeability: People generally use zinc-air batteries as non-rechargeable, while they can recharge lithium-ion batteries hundreds of times.
- Cost: Zinc-air batteries are usually less costly due to lower material costs, whereas lithium-ion batteries are generally more expensive.
- Power Output: Lithium-ion batteries can provide higher power output and are suitable for demanding applications; zinc air batteries may not meet high drain needs.
- Cycle Life: Lithium-ion batteries have a longer cycle life (up to 500-2000 cycles) than zinc-air batteries, typically single-use.
- Environmental Impact: Zinc is less toxic and more abundant than lithium, leading to a smaller ecological footprint for zinc-air batteries.
- Applications: Zinc-air batteries are effective in compact devices like hearing aids, while lithium-ion batteries dominate electric vehicles and consumer electronics.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Zinc-Air Battery | Lithium-Ion Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | Up to 300 Wh/kg | 150-250 Wh/kg |
| Weight | Lighter due to air usage | Heavier due to materials |
| Rechargeability | Generally non-rechargeable | Rechargeable |
| Cost | Usually lower cost | Generally higher cost |
| Power Output | Limited power output | Higher power output |
| Cycle Life | Typically single-use | 500-2000 cycles |
| Environmental Impact | Less toxic, more abundant | More toxic ecological concerns |
| Applications | Hearing aids, military devices | Smartphones, electric vehicles |
Part 4. Advantages of zinc-air and lithium-ion batteries
Advantages of Zinc-Air Batteries
- High Energy Density: Zinc-air batteries can provide a significant amount of energy relative to their weight.
- Cost-Effective: The materials used in zinc-air batteries are generally less expensive than those used in lithium-ion batteries.
- Environmental Friendliness: Zinc is less toxic than lithium, making zinc air batteries more environmentally friendly.
Advantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries
- Rechargeability: Lithium-ion batteries can be recharged hundreds of times, making them ideal for portable electronics.
- High Power Output: They can deliver high currents, making them suitable for demanding applications such as electric vehicles.
- Long Cycle Life: Lithium-ion batteries typically have a longer lifespan than rechargeable batteries.
Part 5. Disadvantages of zinc-air and lithium-ion batteries
Disadvantages of Zinc-Air Batteries
- Non-Rechargeable: Most zinc-air batteries are designed for single use and cannot be recharged.
- Limited Power Output: They may need to provide more power for high-drain applications.
- Humidity Sensitivity: Zinc-air batteries can be affected by humidity, which can impact their performance.
Disadvantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries
- Cost: The materials used in lithium-ion batteries can be expensive, which impacts the overall cost of the devices.
- Environmental Concerns: Lithium mining and battery disposal can pose environmental challenges.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Lithium-ion batteries are sensitive to extreme temperatures, which can impact their performance and safety.
Part 6. Applications of zinc-air and lithium-ion batteries
People primarily use zinc-air batteries in the following ways:
- Hearing Aids: Due to their lightweight and high energy density.
- Military Equipment: For portable devices that require long-lasting power.
- Medical Devices: Such as pacemakers, where reliability is critical.
You commonly find lithium-ion batteries in:
- Consumer Electronics: Smartphones, laptops, and tablets.
- Electric Vehicles: Powering electric cars and hybrid vehicles.
- Renewable Energy Storage: Used in solar energy systems to store excess energy.
Part 7. How to choose between zinc-air and lithium-ion batteries?
- Power Requirements: Opt for lithium-ion for high-drain devices; zinc-air is suitable for low-drain applications.
- Rechargeability Needs: Select lithium-ion when multiple recharge cycles are needed; use zinc-air for single-use devices.
- Cost and Environmental Impact: Zinc-air offers lower cost and eco-friendliness; lithium-ion has broader availability and higher performance.
Common Misconceptions
- “All zinc-air batteries are rechargeable.” — Incorrect; most are single-use primary cells.
- “Lithium-ion batteries are always lighter.” — In reality, zinc-air batteries are lighter by weight but may be bulkier.
Part 8. FAQs on zinc-air vs lithium-ion batteries
How do zinc-air batteries compare to lithium-ion batteries in terms of safety?
Zinc-air batteries use non-toxic materials and have a low risk of overheating, making them generally safer. Lithium-ion batteries require protective circuitry to prevent thermal runaway and fire hazards.
Can zinc-air batteries be recharged?
Most zinc-air batteries are single-use primary cells and are not rechargeable. Rechargeable zinc-air systems are currently in research but are not yet widely available in consumer products.
What is the typical lifespan of a zinc-air battery?
Under normal humidity and low-drain conditions, zinc-air batteries can last from several days to a few weeks. High-drain or extreme humidity environments may shorten their lifespan.
How do I recycle zinc-air batteries?
Zinc-air batteries contain recyclable metal components and can be disposed of at battery recycling centers. Check local recycling programs for proper drop-off locations.
Related Tags:
More Articles

How Long Do Rechargeable AA Batteries Last?
How long do rechargeable AA batteries last? Compare NiMH and lithium AA lifespan, recharge cycles, key factors, and performance vs alkaline batteries.
12V STD vs 12V AGM: Meaning, Differences, and Which Is Better
Understand what STD and AGM batteries mean, their key differences, and which 12V battery fits your needs best in 2026.
Battery Reconditioning Explained: A Comprehensive Guide
Learn what battery reconditioning is, how it works, how long it takes, and when reconditioning chargers are used for lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries.
Recommended 10 Best Batteries For Smoke Detectors
Compare the best batteries for smoke detectors in 2026. See which 9V lithium and alkaline batteries last longest and perform best in smoke alarms.
Triple A Battery Voltage: Everything You Need to Know
How many volts is a AAA battery? See a clear AAA battery voltage chart, compare alkaline, lithium and NiMH cells, and learn how voltage affects device use.