In an era where renewable energy and sustainability dominate global conversations, the search for efficient, cost-effective, and eco-friendly energy storage solutions has never been more urgent. Enter zinc-based batteries—a promising alternative to traditional lithium-ion technology. But what exactly are zinc-based batteries, and could they revolutionize how we power our world? Let’s dive into the science, applications, and potential of this innovative energy storage system.
Part 1. What are zinc-based batteries?
Zinc-based batteries are a category of electrochemical energy storage devices that use zinc as a primary component in their electrodes. Known for their simplicity, affordability, and safety, these batteries have been around for decades but are now gaining renewed attention as advancements address historical limitations.
There are two main types of zinc-based batteries: zinc-air batteries and zinc-ion batteries. Both leverage zinc’s natural properties—high energy density, abundance, and non-toxicity—to deliver power. Unlike lithium, which is rare and requires complex mining processes, zinc is the 24th most abundant element in Earth’s crust, making it a sustainable choice for large-scale applications.
Part 2. How do zinc-based batteries work?
The working principle of zinc-based batteries depends on their type:
Zinc-Air Batteries
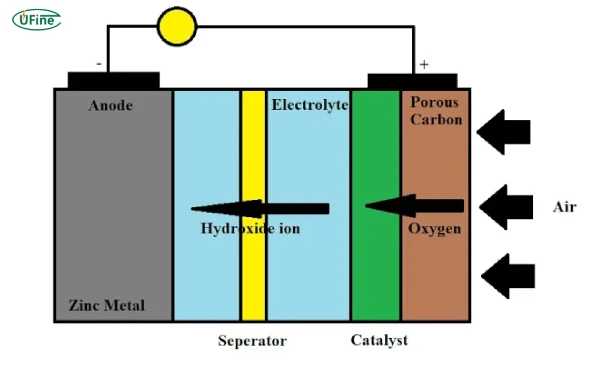
Zinc-air batteries generate electricity through a reaction between zinc and oxygen from the air. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
-
Anode: Made of zinc metal.
-
Cathode: A porous electrode that allows oxygen from the air to react.
-
Electrolyte: Typically an alkaline solution (e.g., potassium hydroxide).
When the battery discharges, zinc at the anode oxidizes, releasing electrons. Oxygen from the air reacts with water and electrons at the cathode, forming hydroxide ions. These ions travel through the electrolyte to complete the circuit, producing electricity.
Zinc-Ion Batteries
Zinc-ion batteries operate similarly to lithium-ion batteries but use zinc ions (Zn²⁺) instead of lithium ions. During discharge:
-
Zinc ions move from the anode (zinc metal) through the electrolyte to the cathode (often a manganese oxide or vanadium-based material).
-
Electrons flow through an external circuit, powering devices.
-
During charging, the process reverses, with zinc ions returning to the anode.
Part 3. Understanding zinc-air batteries
Zinc-air batteries are best known for their high energy density—up to five times greater than lithium-ion batteries in some cases. This makes them ideal for applications where space and weight matter, such as hearing aids, military equipment, and electric vehicles (EVs).
However, traditional zinc-air batteries have limitations:
-
They are typically primary batteries (non-rechargeable), though research into rechargeable versions is advancing.
-
Exposure to air can cause electrolyte evaporation, reducing lifespan.
Recent innovations, such as improved air cathodes and hybrid electrolytes, are addressing these challenges, making zinc-air batteries a contender for grid storage and EV markets.
Part 4. Understanding zinc-ion batteries
Zinc-ion batteries are emerging as a rechargeable alternative to lithium-ion systems. Key features include:
-
Water-based electrolytes: Unlike flammable organic electrolytes in lithium-ion batteries, zinc-ion systems use safer aqueous solutions.
-
High cycle life: Some prototypes achieve over 1,000 charge-discharge cycles.
-
Low cost: Zinc is cheaper than lithium, cobalt, or nickel.
These batteries are being tested for use in renewable energy storage, consumer electronics, and even electric scooters. Companies like Eos Energy Enterprises and NantEnergy are commercializing zinc-ion technology for large-scale applications.
Part 5. Pros and cons of zinc-based batteries
Advantages
-
Safety: No risk of thermal runaway or fires (common in lithium-ion batteries).
-
Sustainability: Zinc is abundant, recyclable, and less environmentally damaging to extract.
-
Cost-Effective: Raw materials are cheaper, and manufacturing processes are simpler.
-
High Energy Density: Especially true for zinc-air variants.
Disadvantages
-
Lower Voltage: Zinc-based batteries typically deliver 1.2–1.6V, compared to lithium-ion’s 3.6V.
-
Limited Cycle Life: Rechargeable versions still lag behind lithium-ion in longevity.
-
Air Sensitivity: Zinc-air batteries require careful sealing to prevent electrolyte degradation.
Part 6. Applications of zinc-based batteries
Zinc-based batteries are already powering niche markets and could expand into broader uses:
-
Medical Devices: Hearing aids and pacemakers (zinc-air).
-
Grid Storage: Storing solar/wind energy (zinc-ion).
-
Transportation: EVs, drones, and electric bikes.
-
Consumer Electronics: Remote controls and emergency backup systems.
In developing countries, zinc-air batteries are being deployed for off-grid solar systems due to their low cost and ease of maintenance.
Part 7. Zinc-based batteries vs. lithium-ion batteries
Here’s how the two technologies stack up:
| Factor | Zinc-Based Batteries | Lithium-Ion Batteries |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lower material/manufacturing | Higher due to rare materials |
| Safety | Non-flammable, stable | Risk of overheating/fires |
| Energy Density | High (zinc-air) / Moderate | Very high |
| Cycle Life | Improving (500–1,500 cycles) | 1,000–3,000 cycles |
| Environmental Impact | Easier to recycle, less toxic | Complex recycling, mining issues |
While lithium-ion dominates today’s EV and portable electronics markets, zinc-based batteries excel in safety, sustainability, and cost—factors critical for grid storage and emerging markets.
Part 8. The road ahead
Zinc-based batteries aren’t just a blast from the past; they’re a gateway to a greener future. With continued R&D focused on enhancing cycle life, energy density, and rechargeability, these batteries could soon compete head-to-head with lithium-ion in multiple sectors. As governments and industries prioritize decarbonization, zinc’s abundance and eco-friendly profile make it a compelling choice for scaling renewable energy adoption worldwide.
Whether you’re an engineer, policymaker, or eco-conscious consumer, zinc-based batteries deserve a spot on your radar—they might just be the missing piece in the clean energy puzzle.
Part 9. FAQs
1. Can zinc-air batteries be recharged, or are they single-use?
Traditional zinc-air cells (e.g., hearing aid batteries) are primary (non-rechargeable), but new rechargeable zinc-air tech achieves 1,000+ cycles.
2. How does humidity affect zinc-based battery performance?
High humidity improves zinc-air efficiency (more O₂ availability), while zinc-ion systems require <80% RH to prevent electrolyte dilution.
3. Can zinc batteries be stacked for higher voltage like lithium packs?
Yes, but requires balancing circuits.
4. Do zinc-ion batteries suffer from “memory effect” like old Ni-Cd cells?
No. Zinc-ion uses dissolution-deposition chemistry, avoiding memory issues.
5. How long do zinc-based batteries last in storage without use?
Zinc-air: 3-5 years (sealed), zinc-ion: 10+ years (dry pre-charged state) vs lithium’s 2-3 years.
6. Are there any toxicity risks if a zinc battery leaks?
Zinc electrolytes are pH-neutral (unlike lead-acid). Leakage poses minimal risk—clean with water .
Related Tags:
More Articles

How to Choose the Best Floor Scrubber Battery for Commercial Cleaning?
Selecting the ideal floor scrubber battery ensures a long runtime, rapid charging, and minimal maintenance for efficient commercial cleaning operations.
Battery for Blower vs Battery for Leaf Vacuum: Which One Should You Choose?
Battery for blower vs leaf vacuum—learn the key differences in power, fit, and runtime to choose the right battery for your outdoor tool needs.
How to Choose the Right Battery for Blower?
Choosing the right blower battery? Consider voltage, capacity, chemistry & usage. This guide helps match the best battery for peak performance.
How to Choose the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries?
Choosing the Best Insulated Battery Box for Lithium Batteries? Discover key factors such as size, material, and safety for optimal protection and performance.
7 Critical Elements on a Lithium Battery Shipping Label
What must be on a lithium battery shipping label? Learn 7 key elements to ensure safety, legal compliance, and correct handling across all transport modes.