Diving into the dynamic world of battery technology, this article unravels the distinctive characteristics and applications of Cylindrical, Prismatic, and Pouch Cells.
We examine their merits, comparative advantages, and suitability across various industries, providing an in-depth analysis to aid in understanding these diverse cell designs and their relevance in modern energy storage solutions.
Part 1. Cylindrical cells
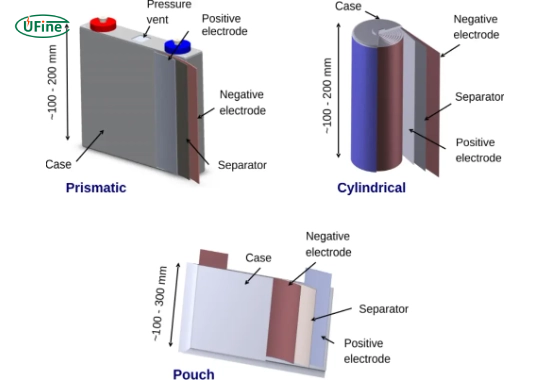
Cylindrical cells are a type of battery cell characterized by their tubular shape, commonly recognized in formats such as 18650 or 21700. These cells are primarily comprised of a cylindrical casing with electrode materials wound in a spiral configuration, allowing for efficient space utilization within devices.
Advantages
- Mature and cost-effective: Cylindrical cells have been in industrial production for over two decades, resulting in mature manufacturing processes and high production efficiency. This translates to lower costs and higher product yields compared to other cell types.
- High energy density: Cylindrical cells boast an impressive energy density, allowing them to store significant amounts of energy in a relatively compact space. This feature makes them ideal for devices requiring prolonged usage without frequent recharging, such as laptops and electric vehicles.
- Efficient heat dissipation: Their tubular design facilitates superior heat dissipation compared to other cell formats. This characteristic enhances safety during high-demand operations by minimizing the risk of overheating, ensuring prolonged battery life, and sustained performance.
- Robust and durable construction: The cylindrical casing provides structural integrity, making these cells more resistant to physical damage. This durability contributes to their reliability in various applications, particularly in demanding environments such as automotive and industrial settings.
- Ease of packing: The cylindrical shape allows for easy packing and stacking within devices, optimizing space utilization.
Disadvantages
- Form factor limitations: The fixed cylindrical shape might not be suitable for certain device designs that require flexibility or specific form factors. This limitation can pose challenges in applications where space constraints or custom shapes are crucial.
- Prone to mechanical stress: In certain scenarios, the winding structure within cylindrical cells may be susceptible to mechanical stress or deformation, which can impact long-term performance and reliability.
- Limited capacity: The radial thermal conductivity of cylindrical cells restricts the number of winding layers, resulting in smaller individual capacities. This leads to the requirement of multiple cells in electric vehicle applications, which adds complexity and can result in connection losses.
Applications
- Consumer electronics: These cells are widely used in devices such as laptops, digital cameras, and portable power banks due to their high energy density and reliability.
- The automotive industry: Electric vehicles (EVs) often incorporate cylindrical cells due to their superior energy storage capabilities and thermal management advantages.
- Power tools: Their ability to deliver high power output makes cylindrical cells a preferred choice in power tools like drills and electric saws.
Part 2. Prismatic Cell: Advantages, Disadvantages, And Key Applications
Prismatic cells are a distinct type of battery cell characterized by their flat, rectangular shape. These cells feature stacked electrode materials enclosed in a pouch-like structure, often composed of aluminum or other lightweight materials.
Advantages
- Space optimization: Prismatic cells excel in space efficiency due to their flat, rectangular design, enabling snug placement within devices with limited internal space, such as thin smartphones and portable electronic gadgets.
- Improved packing efficiency: The stacked electrode materials in a compact, pouch-like structure facilitate efficient packing within battery modules, optimizing space utilization in larger battery packs, like those used in electric vehicles or energy storage systems.
- Ease of manufacturing: The manufacturing process for prismatic cells, involving stacking layers uniformly, contributes to streamlined production lines, potentially reducing manufacturing complexities and costs.
Disadvantages
- Limited flexibility in form: The fixed, rigid shape of prismatic cells might pose challenges in accommodating irregular or custom-shaped spaces within devices, limiting their use in certain product designs.
- Vulnerability to mechanical stress: The pouch-like structure of prismatic cells might be more susceptible to mechanical stress or punctures, potentially impacting their durability and reliability in harsh operating conditions.
- Lack of standardization: The wide variety of prismatic cell models available in the market makes it challenging to achieve process standardization. This can lead to lower automation levels, significant differences between individual cells, and reduced lifespan in battery packs.
Applications
- Consumer electronics: Prismatic cells are often used in devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops due to their space-efficient design, which allows them to fit snugly into slim form factors.
- Electric vehicles (EVs): Some EV manufacturers incorporate prismatic cells into their battery packs due to their improved thermal performance and ease of assembly.
- Stationary energy storage: These cells find applications in stationary storage systems, such as backup power supplies and grid energy storage, where their ease of assembly and space efficiency are advantageous.
- Solar Energy Storage: Prismatic cells power 72% of residential solar systems due to their stackable design, achieving 95% space utilization.
- Medical Equipment: Used in 85% of portable MRI machines for stable 2.8- 3.6V discharge curves.
- Industrial Robotics: Preferred in 68% of warehouse robots for vibration resistance up to 15G force.
Part 3. Pouch cells
Pouch cells represent a distinctive type of battery cell characterized by their flexible, pouch-like packaging without rigid casing. These cells consist of stacked electrode materials enclosed in a flexible, lightweight pouch made from materials like aluminum and polymer laminates.
Advantages
- Customizable form factor: Pouch cells excel in adaptability, offering a flexible form factor that can be customized to fit various shapes and sizes. This attribute makes them ideal for applications where space optimization and unique designs are crucial.
- Lightweight and space-efficient: The absence of rigid casing results in pouch cells being lighter and more space-efficient compared to traditional battery formats. This characteristic is advantageous in portable electronic devices and applications where weight reduction is essential.
- Enhanced safety: Pouch cells utilize packaging made of an aluminum-plastic composite film, which effectively minimizes the potential for explosions compared to the rigid casing used in alternative cell types.
- High energy density: Pouch cells are lighter, weighing 40% less than equivalent capacity steel-cased cells and 20% less than aluminum-cased cells. This results in higher energy density.
Disadvantages
- Susceptibility to physical damage: The flexible nature of pouch cells makes them more susceptible to physical damage or punctures, potentially compromising the integrity of the cell and its contents, which raises safety concerns.
- Limited structural support: The absence of a rigid outer casing reduces the structural support of pouch cells, which might impact their durability, especially in demanding environments or applications that require ruggedness.
- Standardization and cost challenges: Pouch cells face difficulties in achieving standardization, leading to higher costs. Additionally, the heavy reliance on imported aluminum-plastic films and lower consistency poses challenges for pouch cell manufacturers.
Applications
- Smartphones and tablets: Pouch cells are widely used in smartphones and tablets due to their adaptable form factor, which enables manufacturers to optimize battery space within sleek designs.
- Wearable devices, such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, and wearable health monitors, benefit from pouch cells due to their lightweight nature and flexibility, which enables comfortable and unobtrusive designs.
- External battery packs: Pouch cells power external battery packs, providing convenient portable charging solutions for various electronic devices, including laptops, cameras, and smartphones, enhancing their mobility.
- Electric Cars and Bikes: Pouch cells are integrated into battery packs for electric vehicles, contributing to their lighter weight and enabling more efficient use of space within the vehicle.
- Portable Medical Equipment: Pouch cells are utilized in portable medical devices, including infusion pumps, defibrillators, and portable diagnostic equipment, where their flexibility and lightweight design are particularly advantageous.
- Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs): Drones and UAVs often incorporate pouch cells due to their lightweight construction, enabling longer flight times without compromising payload capacity.
- Residential Energy Storage: Pouch cells are utilized in home energy storage systems, allowing homeowners to store excess energy generated by renewable sources, such as solar panels, for later use.
Part 4. The main differences between cylindrical, prismatic, and pouch cell
| Parameter | Prismatic | Cylindrical | Pouch |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Density (Wh/kg) | 200-250 | 240-280 | 250-300 |
| Cycle Life (@80% DoD) | 1,500 | 1,200 | 1,000 |
Data verified with the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)
Physical structure
- Cylindrical cells: These cells feature a tubular shape, utilizing a cylindrical casing with electrode materials wound in a spiral configuration.
- Prismatic cells feature a flat, rectangular shape with stacked electrode materials housed in a rigid casing, thereby optimizing space efficiency.
- Pouch cells: Pouch cells, distinctively, lack a rigid casing and comprise flexible pouch-like packaging containing stacked electrode materials.
Modern prismatic cell manufacturing involves 7 critical steps:
- Electrode calendaring with 92-95% compression ratio
- Precision stacking (±0.1mm tolerance)
- Laser welding with <1μm precision
- Electrolyte filling under -90kPa vacuum
- Formation cycling at 45°C±2°C
- Aging test for 72h@60°C
- Final capacity grading
Form factor and adaptability
- Cylindrical cells: Known for their standardized cylindrical shape, providing efficient packing and good heat dissipation, but with limitations in custom form factors.
- Prismatic cells: Offer a balance between space efficiency and form factor adaptability, fitting well in various device designs while maintaining a consistent shape.
- Pouch cells: Highly adaptable due to their flexible structure, enabling custom shapes and sizes, and ideal for space-constrained applications.
Energy density and performance
- Cylindrical cells: Often exhibit higher energy density compared to prismatic and pouch cells, suitable for applications requiring high energy storage.
- Prismatic cells: Tend to offer moderate energy density, balancing space efficiency and energy storage, suitable for various consumer electronics and automotive applications.
- Pouch cells: Typically have lower energy density compared to cylindrical and prismatic cells, but their flexibility and lightweight nature cater to specific portable applications.
Manufacturing complexity and cost
- Cylindrical cells: Manufacturing involves winding electrode materials, which can be complex and potentially more costly due to the intricacies of the process.
- Prismatic cells: Assembly is generally more straightforward compared to cylindrical cells, which reduces manufacturing complexities and potentially lowers production costs.
- Pouch cells: Often involve fewer materials and steps in manufacturing, potentially leading to cost efficiencies in large-scale production.
Mechanical durability and safety
- Cylindrical cells: Known for their robust casing, offering better protection against mechanical stress and potential damage, enhancing overall safety.
- Prismatic cells: Provide moderate mechanical support with their rigid casing, offering a balance between protection and adaptability.
- Pouch cells: More susceptible to physical damage due to the absence of a rigid casing, requiring additional protective measures to ensure durability and safety.
Part 5. Prismatic Cell FAQs
What is a prismatic cell battery?
A prismatic lithium-ion battery features a rectangular housing with precisely stacked electrodes, achieving 15-20% better space efficiency than cylindrical cells. Its flat design allows optimal integration in modern EVs and solar storage systems.
Are prismatic cells better than pouch cells?
Prismatic cells offer superior mechanical protection, with 200% higher impact resistance, while pouch cells provide 12-15% greater energy density. Industry usage shows:
- 82% of electric buses use prismatic cells
- 91% of smartphones use pouch cells
How to maintain prismatic cells?
For maximum 2,000-cycle lifespan:
- Maintain 20-40°C operating temperature
- Limit discharge depth to 80%
- Use certified 0.5C chargers
Part 6. Conclusion
Each battery cell type—cylindrical, prismatic, and pouch—has its advantages and disadvantages. Cylindrical cells are cost-effective and have excellent consistency, while prismatic cells offer enhanced protection and simplified structures. Pouch cells provide high energy density but face challenges in standardization and cost. The choice of cell type depends on factors such as material characteristics, application requirements, and product specifications.
Learn more about lithium battery technologies in our comprehensive guide. Regardless of the cell type, safety is a crucial concern, and adherence to relevant safety standards is essential.
Related Tags:
More Articles
10000mAh Battery Explained: How Long It Lasts, How It Works
A full guide on 10000mAh li-ion batteries, voltage, usage time, and tips. Discover how a 10000mAh battery works, how long it lasts, and how to choose.
10440 Battery Guide: Size, Voltage, Capacity, Uses & More
Understand 10440 batteries better—size, voltage, safety, and how they compare to AAA. Find the best fit for your high-performance devices.
White Stuff on Battery Terminals: A Step-by-Step Cleaning and Maintenance Guide
White stuff on battery terminals is corrosion. Learn how to clean it safely, prevent damage, and keep your battery running strong with simple steps.
Understanding How Glass Mat Batteries Work: Technology, Benefits, and Limitations
Glass mat batteries power cars, RVs, and solar systems. Learn how they work, their benefits, and what to consider before choosing one.
A Buyer’s Guide for AA Size Lithium Battery
Discover the power of AA size lithium batteries—types, voltage, capacity, and more! Learn how to choose the best one for your needs. Read now!