Batteries are integral to modern life, powering everything from remote controls to electric vehicles. However, the improper disposal of batteries poses significant environmental risks. Understanding how to discard batteries and protect the environment adequately is a matter of compliance and a crucial step toward sustainable living. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of battery disposal, its environmental implications, and actionable steps you can take to minimize your ecological footprint.
Part 1. Understanding the types of batteries
The first step towards proper battery disposal is recognizing the different types of batteries and their specific disposal requirements. Each type of battery contains unique materials and chemicals that necessitate tailored disposal methods.
Alkaline Batteries
Alkaline batteries, commonly used in household items such as toys, remote controls, and flashlights, are the most ubiquitous. They once contained mercury, but modern versions are mercury-free.
Lithium-ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are the powerhouse behind most rechargeable electronics, including smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles. Their high energy density and rechargeability make them famous but also contain potentially harmful substances.
Nickel-Cadmium (NiCd) Batteries
Various rechargeable devices and tools use nickel-cadmium batteries. They contain cadmium, a heavy metal toxic to the environment and human health.
Lead-Acid Batteries
Automotive applications and industrial equipment predominantly use lead-acid batteries. They are highly recyclable but pose significant environmental hazards if not handled correctly.
Button Cell Batteries
Button cell batteries, found in watches, hearing aids, and small electronics, often contain mercury. Despite their small size, their potential for environmental harm is substantial.
Part 2. Why do batteries need to be appropriately disposed of?
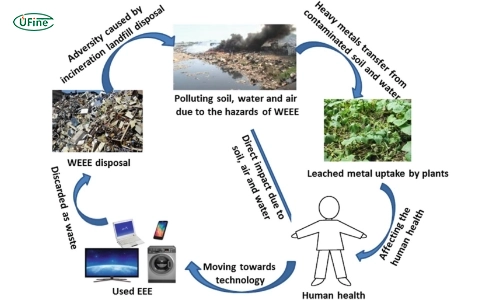
The environmental repercussions of improper battery disposal are multi-faceted, impacting soil, water, air quality, wildlife, and human health.
1. Soil and Water Contamination
Batteries contain heavy metals such as lead, cadmium, and mercury. When disposed of improperly, these metals can leach into the soil and groundwater, leading to long-term contamination of ecosystems and drinking water sources.
2. Air Pollution
Incinerating batteries as a disposal method can release toxic fumes, contributing to air pollution. These emissions can include heavy metals and other harmful compounds affecting the environment and human health.
3. Wildlife Harm
Wildlife is at significant risk from improperly disposed batteries. Animals can ingest battery fragments, leading to poisoning, internal injuries, and death. The contamination of natural habitats further disrupts ecosystems.
4. Human Health Risks
Exposure to the toxic substances in batteries, whether through contaminated water, soil, or air, can lead to severe health issues. These include neurological damage, kidney disease, and various forms of cancer.
Part 3. How do you properly discard batteries?
Proper battery disposal varies depending on the type of battery. Here are specific guidelines to follow:
1. Alkaline Batteries
In many regions, alkaline batteries can be disposed of with regular household trash due to the absence of mercury. However, recycling is still preferred to recover materials and reduce waste. Always check local regulations for specific guidelines.
2. Recycling Lithium-Ion Batteries
Never throw lithium-ion batteries in the trash. Recycling programs are widely available through electronics retailers, manufacturers, and municipal collection events. These programs ensure the recovery of valuable materials and the safe management of hazardous substances.
3. Handling Nickel-Cadmium Batteries
Due to the toxic cadmium content, it is essential to recycle NiCd batteries. Specialized recycling facilities equip themselves to handle these batteries safely, preventing environmental contamination.
4. Disposing of Lead-Acid Batteries
Laws require many automotive shops and recycling centers to accept lead-acid batteries because they are highly recyclable. Proper recycling prevents lead contamination and allows for the recovery of valuable materials.
5. Safe Disposal of Button Cell Batteries
Take button cell batteries to hazardous waste disposal facilities due to their mercury content. Specialized recycling programs can safely handle these batteries, mitigating their environmental impact.
Part 4. Battery recycling programs
Several recycling programs facilitate the safe disposal of batteries, ensuring they do not end up in landfills.
1. Manufacturer Take-Back Programs
Many battery manufacturers offer take-back programs, providing consumers with a convenient way to return used batteries for recycling. These programs are often free and aim to increase the recycling rate of hazardous batteries.
2. Community Collection Events
Local governments frequently organize community collection events where residents can drop off hazardous waste, including batteries. These events are often part of broader environmental initiatives and provide a safe, controlled environment for collecting and properly disposing of hazardous materials.
Part 5. Preparing batteries for disposal
It is crucial to properly prepare batteries for disposal to prevent accidents and ensure safe handling.
1. Tape the Terminals
Before disposing of batteries, especially lithium-ion and lead-acid types, it is essential to tape the terminals. This prevents short-circuiting, which can cause fires or explosions during transport and handling.
2. Store in a Cool, Dry Place
Store used batteries in a cool, dry place until you are ready to dispose of them. This reduces the risk of leakage and ensures they remain stable.
3. Label Your Batteries
Clearly label the types of batteries you are storing. This helps recycling centers quickly identify and process them correctly, ensuring they manage them according to their specific disposal needs.
Part 6. Battery recycling legislation and regulations
Understanding battery disposal’s legal framework helps ensure compliance and promotes environmental protection.
1. Federal Regulations
The Battery Act of 1996 established guidelines for adequately disposing and recycling batteries in the United States, particularly those containing hazardous substances like mercury, cadmium, and lead.
2. State and Local Laws
Many states have enacted stricter battery disposal laws. For instance, California’s Universal Waste Rule mandates recycling all household batteries. It’s essential to be aware of your local regulations to ensure compliance.
3. International Regulations
Countries worldwide have different regulations regarding battery disposal. The European Union’s Battery Directive, for example, imposes strict recycling rates and prohibits the disposal of batteries in household waste. Staying informed about international standards is crucial for global environmental protection efforts.
Part 7. Innovative battery recycling technologies
Advancements in recycling technologies are making battery disposal more efficient and environmentally friendly.
1. Mechanical Processes
Mechanical recycling involves physically breaking down batteries to recover materials such as metals, plastics, and chemicals. This method is efficient but requires sophisticated machinery to handle different battery types.
2. Pyrometallurgical Processes
These high-temperature processes extract metals from batteries by melting them down. While effective, they require significant energy and can produce harmful emissions if not carefully managed.
3. Hydrometallurgical Processes
Hydrometallurgical processes use acids and other chemicals to separate and recover valuable materials from batteries. This method is often more environmentally friendly than pyrometallurgy but requires careful handling of hazardous substances.
관련 태그:
더 많은 기사

12 Volt Batteries: How Long Can They Really Last?
Discover how long a 12-volt battery lasts, factors affecting its lifespan, and tips to extend its life.
Upgrade Your Drill Battery to Lithium Batteries
Discover why switching from Ni-Cd to li batteries for your drill is essential. Learn about battery types, comparisons, and how to choose the best drill battery.
Everything You Need to Know About Group 26 Batteries
Discover the ins and outs of Group 26 batteries, including types, dimensions, prices, and maintenance tips. Learn where to buy the best Group 26 battery.
Recommended 10 Leisure Batteries for Motorhomes or Caravans
Traveling in a motorhome or caravan? A good leisure battery is essential. Avoid power issues with our guide to the top 10 best leisure batteries for this year.
Top 10 Truck Battery Options to Keep You Rolling Strong
Struggling with weak truck batteries? Avoid breakdowns with our guide to the top 10 truck batteries, ensuring durability and high performance for any journey.