Lithium battery packs are vital in many modern devices, powering everything from smartphones to electric vehicles. However, understanding what the letters “S” and “P” mean on a lithium battery pack can be confusing. This article clarifies these terms and explains their significance in battery pack design.
Part 1. Understanding lithium battery pack
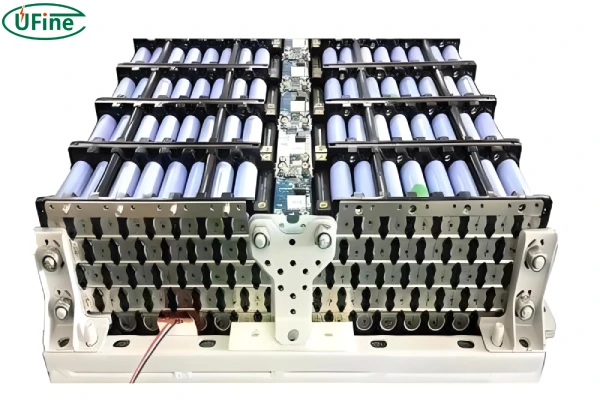
A lithium battery pack is a combination of individual lithium-ion cells. These cells work together to provide the necessary power for various applications. How these cells are connected—whether in series, parallel, or a combination of both—determines the overall voltage and capacity of the battery pack.
Components of a Lithium Battery Pack
- Cells: The fundamental units that store and release electrical energy.
- Battery Management System (BMS): Ensures safe operation by monitoring temperature, voltage, and current.
- Connectors: Facilitate the series and parallel connections of cells.
- Casing: Provides structural integrity and protection for the cells and electronics.
Part 2. What does the S on a lithium battery pack mean?
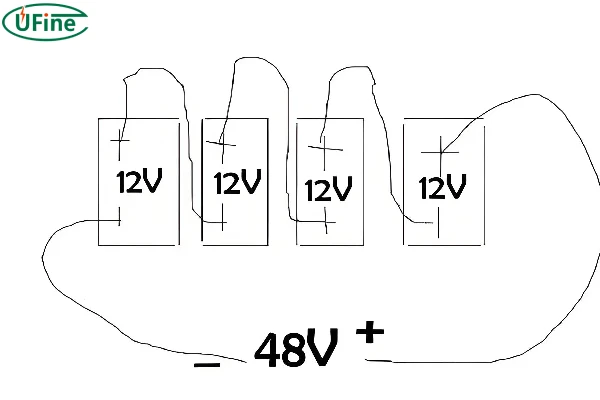
The “S” in a lithium battery pack stands for “Series.” It indicates the number of cells connected in series. For instance, a 3S battery pack has three cells connected in series. If each cell is 3.7V, the total voltage of the pack is 11.1V (3.7V x 3). The main advantage of series connections is the increase in voltage, which is necessary for applications requiring higher power.
Part 3. What does the P on a lithium battery pack mean?
The “P” in a lithium battery pack is “Parallel.” It denotes the number of cells connected in parallel. For example, a 3P battery pack has three cells connected in parallel. If each cell has a capacity of 2000mAh, the total capacity of the pack is 6000mAh (2000mAh x 3). Parallel connections are beneficial for increasing the battery pack’s capacity and thus extending the device’s operating time.
Part 4. What are the ways to connect the lithium cells?
The performance and characteristics of a lithium battery pack depend on how the individual cells are connected. There are three primary connection methods: series, parallel, and series-parallel.
1. Series Connection
In a series connection, the positive terminal of one cell is connected to the negative terminal of the next cell. This setup increases the overall voltage of the battery pack. For example, connecting three 3.7V cells in series results in a battery pack with a total voltage of 11.1V (3.7V x 3).
2. Parallel Connection
In a parallel connection, all the positive terminals of the cells are connected, and all the negative terminals are connected together. This configuration increases the total capacity (mAh) of the battery pack while keeping the voltage the same as a single cell. For instance, connecting three 3.7V cells with 2000mAh each in parallel results in a 3.7V battery pack with a capacity of 6000mAh (2000mAh x 3).
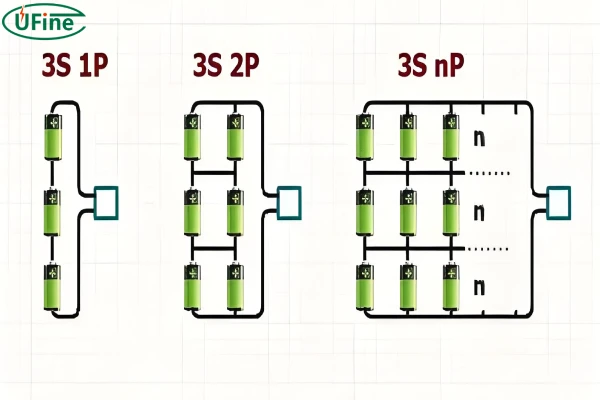
3. Series-Parallel Connection
The series-parallel method combines both series and parallel connections. It increases both the voltage and capacity of the battery pack. Cells are first connected in series to achieve the desired voltage. Then these series strings are connected in parallel to boost the capacity. For example, a 3S2P configuration means three cells in series in each string, and two such strings are connected in parallel.
Part 5. Why do li packs need to be connected in series, parallel, or series-parallel?
Lithium battery packs need these connection methods to meet the specific voltage and capacity requirements of different applications.
- Series Connection: Increases the voltage to match the requirements of high-voltage devices such as power tools and electric vehicles.
- Parallel Connection: Increases the capacity to extend the battery life of devices like smartphones and laptops.
- Series-Parallel Connection: Balances both voltage and capacity, providing flexibility for various applications, including high-performance drones and electric bikes.
Part 6. Series vs parallel vs series-parallel
Let’s compare these connection methods to understand their differences better:
| 기능 | Series (S) | Parallel (P) | Series-Parallel (S-P) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage Increase | 예 | 아니요 | 예 |
| Capacity Increase | 아니요 | 예 | 예 |
| Complexity | Simple | Simple | Complex |
| Use Case | High voltage devices | Long battery life | Versatile applications |
| Failure Impact | Higher risk | Lower risk | Medium risk |
| Balancing Needs | 높음 | 낮음 | Medium |
| Example Configuration | 3S1P (11.1V 2000mAh) | 1S3P (3.7V 6000mAh) | 3S2P (11.1V 4000mAh) |
| Application Example | Power tools | Power banks | Electric vehicles |
By understanding these connection methods, you can appreciate how they impact the performance and application of lithium battery packs. This knowledge is crucial for designing and working with battery-powered devices, ensuring they meet the desired specifications and performance standards.
관련 태그:
더 많은 기사

Top 10 3.2 Volt LiFePO4 Batteries in 2024
Do you need a 3.2-volt battery for a customized battery pack or an electric device? This top 10 3.2 volt LiFePO4 battery guide will explore key aspects of all batteries.
Top 10 Travel Trailer Battery Review 2024
Find out the top 10 travel trailer batteries of 2024. Featuring the most advanced and hot-selling options. So you can choose the best travel trailer battery.
Upgrade Your RV with LiFePO4 Batteries
Discover why LiFePO4 batteries are the best choice for your RV. Learn about their advantages, costs, lifespan, and more in our detailed guide.
Choosing the Best Deep Cycle Lithium Battery for Your Camper
Discover the best deep cycle lithium batteries for campers. Learn about voltage, capacity, size, price, and lifespan to power your adventures.
Choosing the Best Lithium Ion Battery for Your Motorhome
Learn about lithium ion motorhome batteries: types, capacity, voltage, sizes, prices, and lifespan. Discover the best battery for your RV needs.